Commodity Futures Basics (& Supply Chains)
This is a post to consolidate my own learning on the basics of commodity futures. Especially now with tariffs/TACO, understanding the delivery mechanism, specs and supply chain of each contract is important.
- Energy - B, CL, HO, RB, NG.
- Metals - HG, ALI, HRC
- Ags (Grains) - ZC, ZS, ZW, ZR
- Ags (Softs, Produce) - SB, CC, KC/RM, LE, OJ
- Macro (Selected) - SR, E6, ES
Material from X, substack, ChatGPT, etc.
Supply Chain
Relative to other industries (e.g say chips), quite simple. About optimizing logistics via arbitrage (geographical, temporal, form).
Exchanges
Where the matching engine/orderbook lives. The hierarchy is group, exchange, venue.
CME Group: CME/NYMEX/CBOT/COMEX
Data center in Aurora, Illinois, West of Chicago/Lake Michigan, 41.7962, -88.2426.
Exchange datacenters are all in Equinix DC3, but the exchanges/listings are divided due to legacy reasons.
Venues: Globex = CLOB matching engine, ClearPort = bilateral trades (EFP, block trades), and Floor = legacy physical pits.
- CME: FX futures, equity index futures (S&P, Russell)
- NYMEX: Oil (across the barrel, crude, LPG, gasoline, diesel, fuel oil, petchems), Gas (NG/HH), domestic US power and gas futures.
- CBOT: Grains & oilseeds (corn, wheat, soybean), produce (cattle, hogs, milk, cheese), lumber
- COMEX: Precious (gold, silver, platinum, palladium), base (copper, aluminium, zinc), ferrous (iron, steel), battery (cobalt, lithium)
ICE Group
ICE Group: IFEU, IFAD, IFED, IFUS.
- IFEU (LIFFE): Brent, European oil & products
- Ice Endex: TTF, European gas
- IFUS (NYBOT): Softs (sugar, cocoa, cotton), produce (OJ), intl FX, etc
- IFAD (Abu Dhabi): East oil & products, etc
- IFED (US Energy Division): Domestic US gas
IFEU datacenter called EULC seems to be in Basildon, Essex, East of London, 51.5873, 0.4956. For IFUS (softs orderbook), it’s either in Chicago or Atlanta.
Other
- EU - EEX (Power, gas, carbon credits, freight, ags), LME (same as SHFE), BUCE (Belarius Universal Commodity Exchange - metals, timber, ags), Euronext (Corn, wheat, salmon, rapeseed)
- APAC China - SHFE/INE (Metals - Copper, ali, zinc, lead, nickel, tin, gold, silver, steel product, crude, LSFO, FO, bitumen, rubber), DCE (Dalian Exchange - Ags: corn, soybean, egg, wood, rice, palm oil, hogs, petchem, plastics, LPG, coal, iron ore), ZCE (Zhengzhou - Ags: cotton, wheat, sugar, rapeseed, fruit, glass, urea, methanol, soda ash, etc)
- APAC ME - DME (Oman crude), IME
- APAC RoW - TOCOM, SGX (freight, iron, coal, refined products), MCX/NCDEX (India)
- LATAM - B3SA (Brazil - Ags: Coffee, corn, ethanol, cattle, soybean)
Brokers/Execution Engine/Protocols
To trade, you need a broker (FCM - futures commission merchant) and an OMS/EMS/execution platform like TT to send orders to datacenter.
Brokers aggregate participants and authorize gateway to exchange in a regulated fashion, so you interact with CLOB within the broker’s regulatory framework.
For examples, FCM brokers might be Marex, StoneX, Macquarie, RJO, etc. You as a trading participant have a relationship/account with a broker. This account lets you login/authorize into an EMS/OMS platform like TT.
A broker is responsible for:
- Exchange access/membership
- Clearing/settlement: margin account, PnL/MTM.
- Risk control: position/exposure limits, delivery prevention
Platform = API + GUI to interact with corresponding matching engine/orderbook, regulated by a broker.
Orders
Set of primitives that defines how you interact with other participants in the orderbook. CME Globex Order Types. Clients communicate with exchange via messaging protocol like FIX.
Orderbook consists of price levels (1c or 0.01c) on either side (where each level has a queue), each level is blocks of one lot of more orders.
- Limit - Max bid, min offer at limit price. Either executed, cancelled, or expires. Any portion matched immediately executed.
- Market Limit - Best bid, best offer. If partially filled, becomes limit order at limit price.
- Market Limit with Protection - Market limit with protection points, matches order at best price without exceeding protection limit.
- Stop Limit - Only goes into book when trigger price is traded, then goes into book at limit price.
Also qualifiers build on duration (required), minimum execution qty (optional), display qty (optional). From there, you have good till cancel, good till date, fill and kill, fill or kill.
Exchanges are massive servers with specific messaging protocols communicating with market participants. For an instrument, no true concurrency, everything is a (very fast) queue. One long deterministic sequence of events at nanosecond frequency, any tiebreakers are resolved with tiebreaking rules to maintain a single queue.
Volume, OI, Calendar
Volume = num transactions over time window. OI = num open contracts. Given atomic matched transaction (matched by engine/CLOB via price-time priority) gives these scenarios:
- OI increases if both parties open exposure in opp directions (e.g. A net long buys 1 and B flat sells 1, or A flat buys from B flat)
- OI decreases if both parties close exposure in opp directions (e.g. A net long sells 1 and B short buys 1)
- OI remains same if both transacting parties are net same dir (e.g A net long buys/sells 1 from B net long)
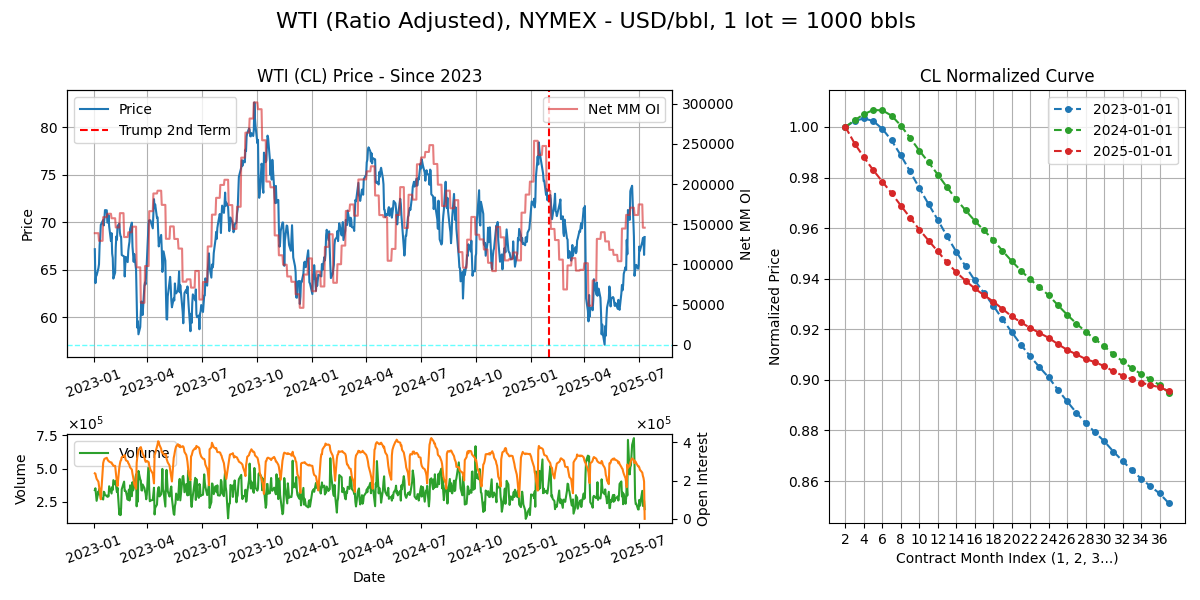
Taking a look at WTI July and August contracts:
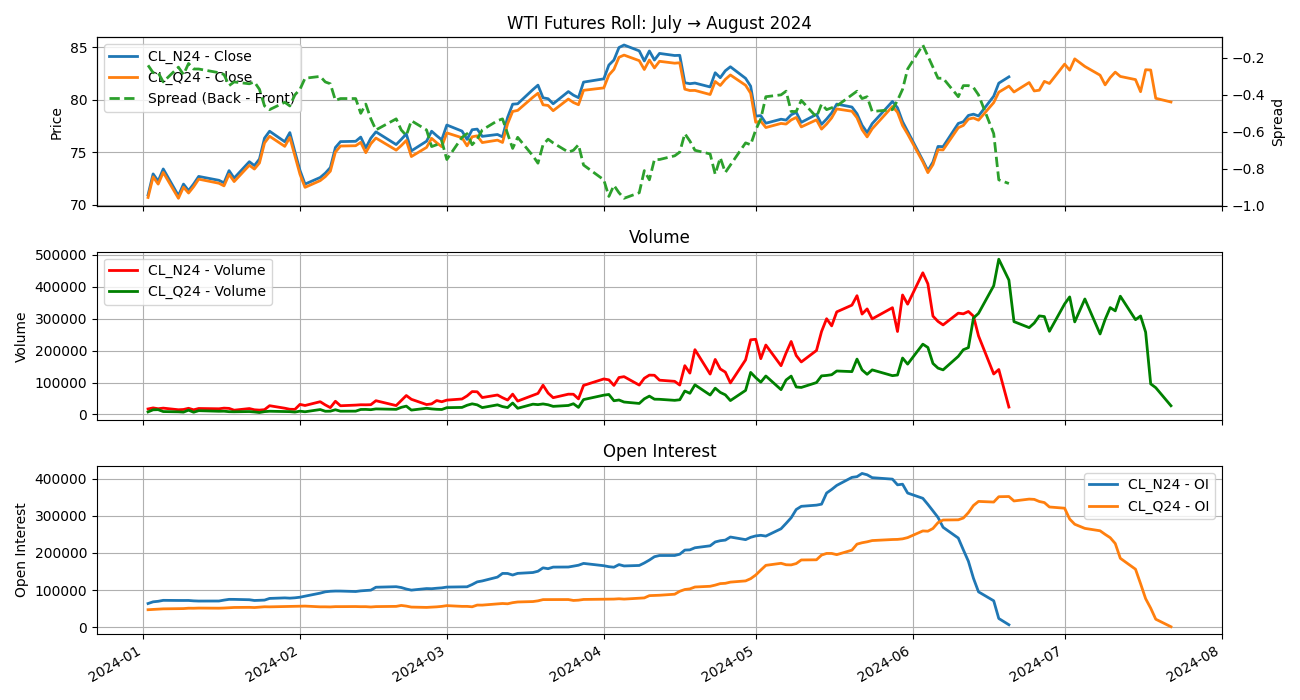
OI climbs 3M before as more participants open trades. Rolling begins in the first few weeks of prior month. Zooming into prior month:
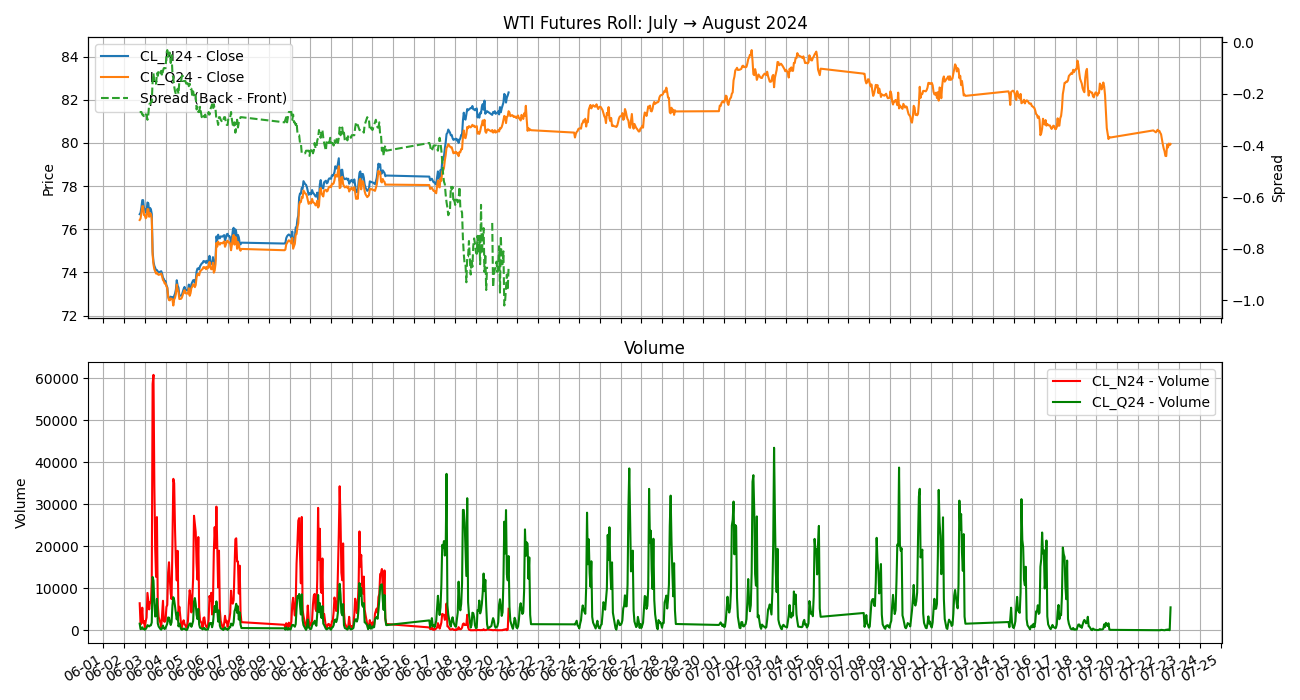
Volume drop in the weeks of June as non hedgers close out their position. Interestingly, the intraday volume shows 2 peaks: London morning (9am UK / 4am EST), the US morning (9am EST) - aka people trade working hours.
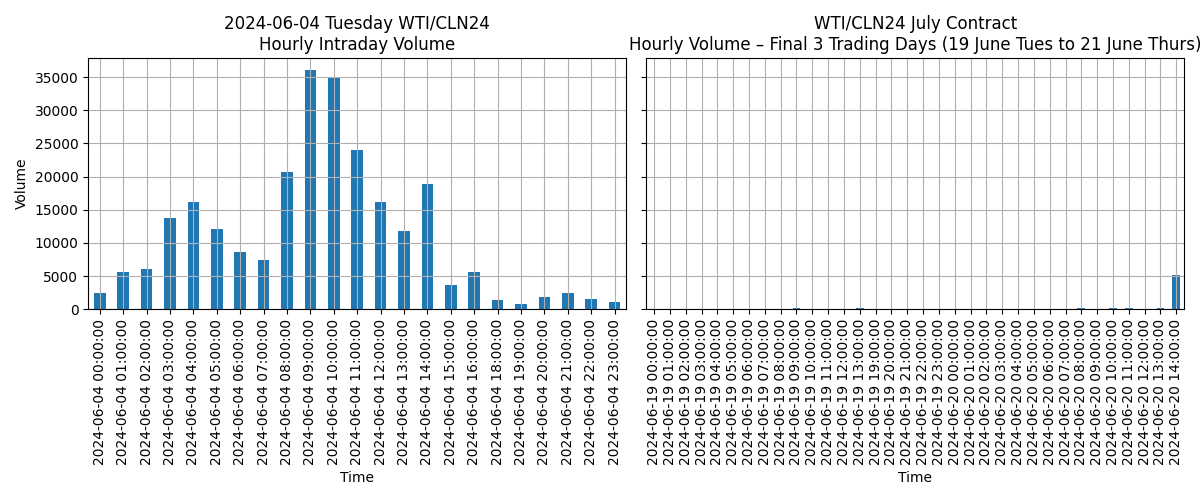
On last day of the contract (20th) a spike in volume occurs with 5000 lots / 5m barrels / 2 Vs changing hands. Probably trading houses trading in window for delivery. Now for Cocoa:
Roll and Backadjustment
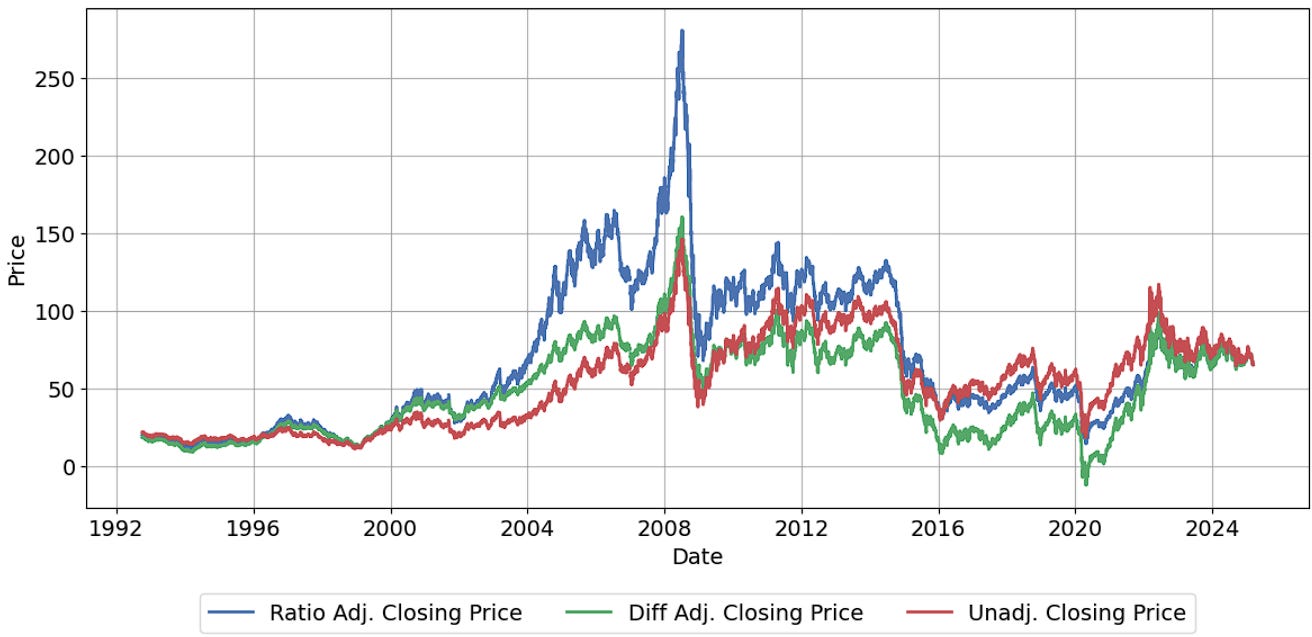
Systematic models need a single time series. This chart is from 2 Quants (Takahe Capital) of 3 different types of backadjustment.
Anchoring from the most recent contract, in contango, you multiply up (ratio) / shift up (absolute) all previous contracts cumulatively by the price difference at your roll day. Farther back the contract = more it gets adjusted.
Specs, Delivery
To get a feel of specs, calendars, delivery mechanisms and trading behavior of some futures contracts I will use the FRD 130 most active futures bundle:
- Calendar
- Specs
- Delivery mechanism
- Supply chain
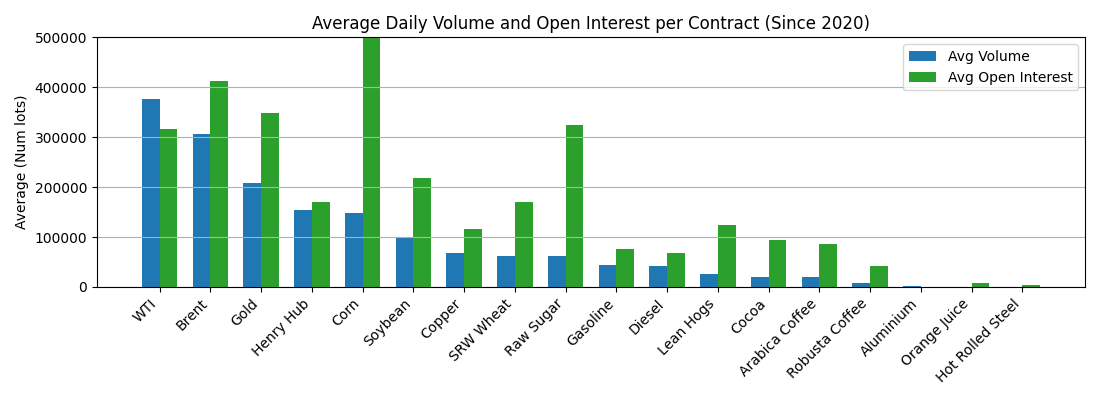
ADV/OI since 2020: Oil, then gold then gas. For ags, corn and soybean. Softs less, most in raw sugar.
To get a feel of vol per lot, I take std of price ($) since 2020 x contract multiplier
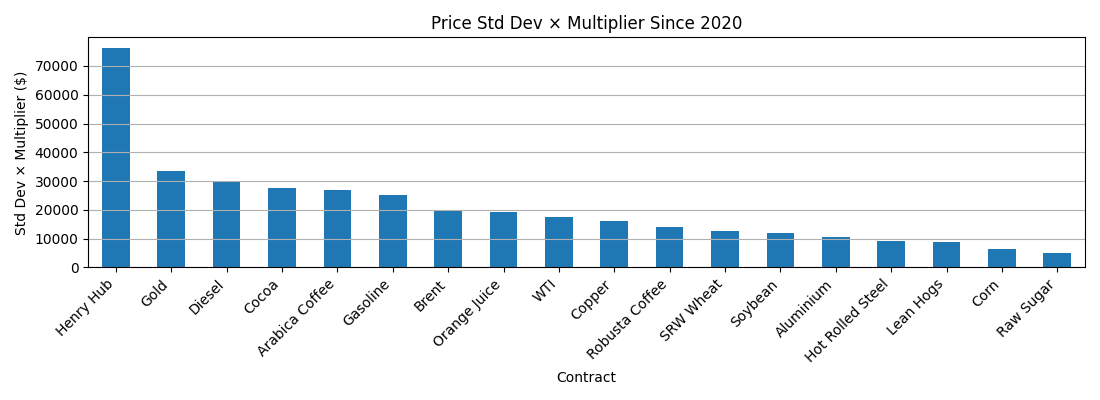
Gas dominating due to 2022 being included in the dataset.
Use Case
- Lock in revenues/costs (hedging).
- Take/make delivery
- Speculate/provide liquidity & price discovery to hedgers.
Oil
Numeracy
- Oil Avg Daily Production - 100mn = 50V
- Oil Avg Daily Inventory - 3500-4000 mn / 4 bn = 2000V
- Avg Daily Build/Draw - 1mn
- Oil/Products On Water - 1500-1800mn / 1.5bn = 750V
Brent (B)
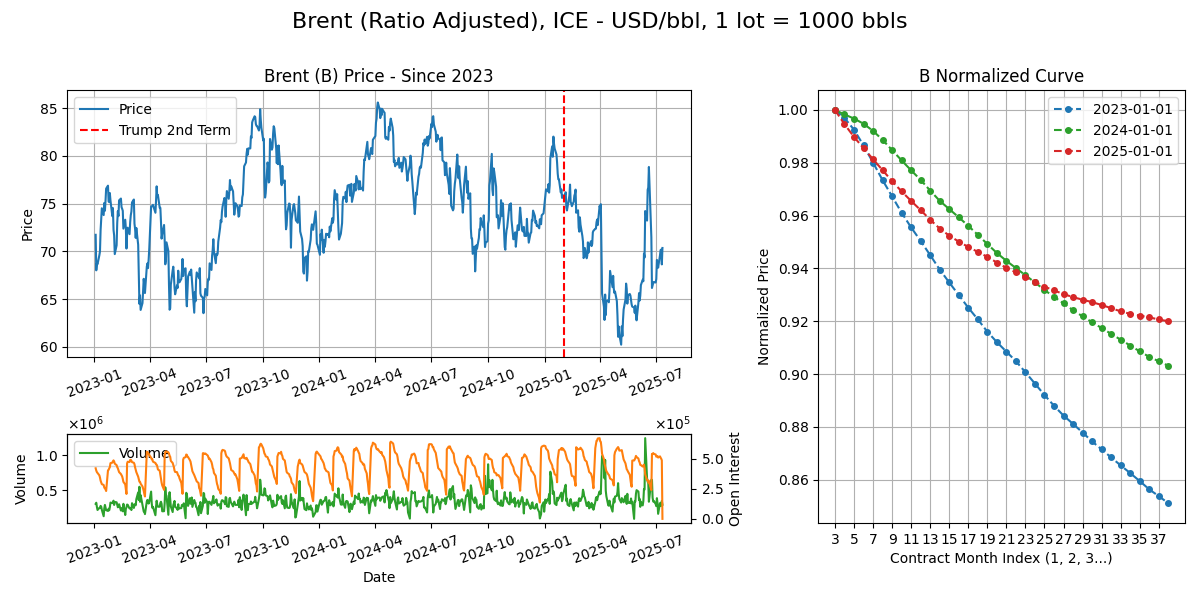
Calendar - 7Y ahead, monthly, trading stops last BD M-2 (March expires in Jan). Weekdays except 11pm-12am GMT
Delivery - EFP with option cash settle on ICE Brent Index, FOB Sullom Voe in Shetland Islands (excluding WTI Midland). Pipelines in North Sea into various terminals
WTI (CL)
Calendar - 10Y ahead, monthly, trading stops 3 BD before 25th of M-1 (e.g Feb expires in Jan). Weekdays except 10pm-11pm GMT. Ordinary OPEC meetings June and Dec bi-annual.
Supply Chain
Major Export/Import: Export: ME (35%), Russia (10%), US (10%), WAF (8%), SA (8%), North Sea (5%), Caspian (5%). Import: Asia (China 25%, India 10%, Japan 8%, SK 6%, etc) 65%, EU (20%), Americas (5%), Africa (5%) etc.
Worth noting that oil production (due to technical and economic reasons) is ‘sticky’, it is difficult to quickly increase or decrease production from the drilling/rig/field perspective. Pricing/selling done via markets, benchmarks or OSP.
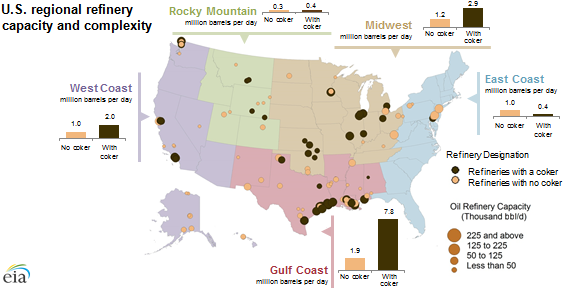
Refined Products: Light distillates (LPG, gasoline, naphtha), mid distillates (jet fuel, diesel), heavy distillates (fuel oil, marine fuel, lubricants, asphalt).
Refineries: Prefer a specific crude slate/composition (taste) due to CDU structure, and produce an optimized product slate, which is adjustable (many moving parts) based on economics/margins.
Production: Held steady at % capacity in kbld, left spare capacity, cuts/increases following planned long term schedule (in case of OPEC+). Any residual/excess demand goes to draw/builds in inventory.
Heating Oil / ULSD (HO)
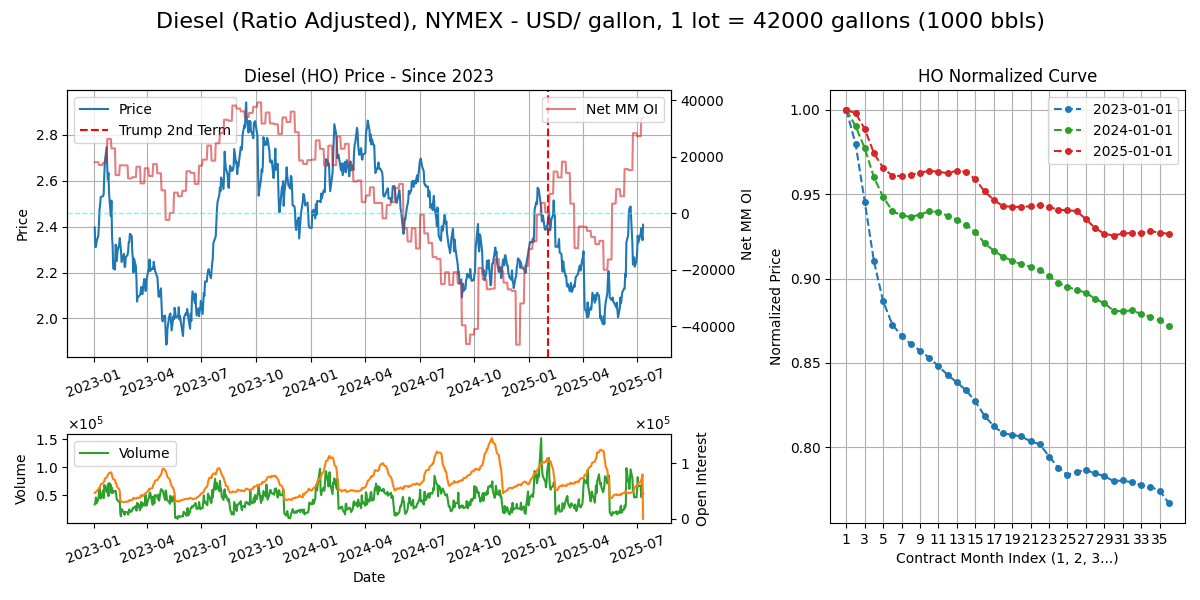
Calendar - 3Y ahead monthly contracts. Trading stops last BD of M-1. Weekdays except 11pm-12am GMT.
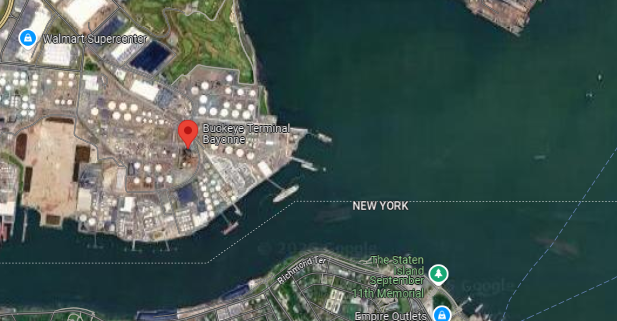
Delivery - This contract represents the domestic east coast US diesel market (population center). Delivery comes by pipeline say from Gulf or barge from and some Europe/ARA cargoes TA to various terminals in NY harbour. Then distributed out via rail/truck etc to gas stations, industrial uses, power plants.
Curve Structure - Some slight seasonality in the winter months but not as much as RBOB Gasoline. Heating demand should explain this.
Supply Chain
Export/Import: Export: ME (20%), India (15%), USGC (15%), Russia (10%), Asia (20%), other. Import: EU (30%), Africa (20%), Latam (20%), other
RBOB Gasoline (RB)
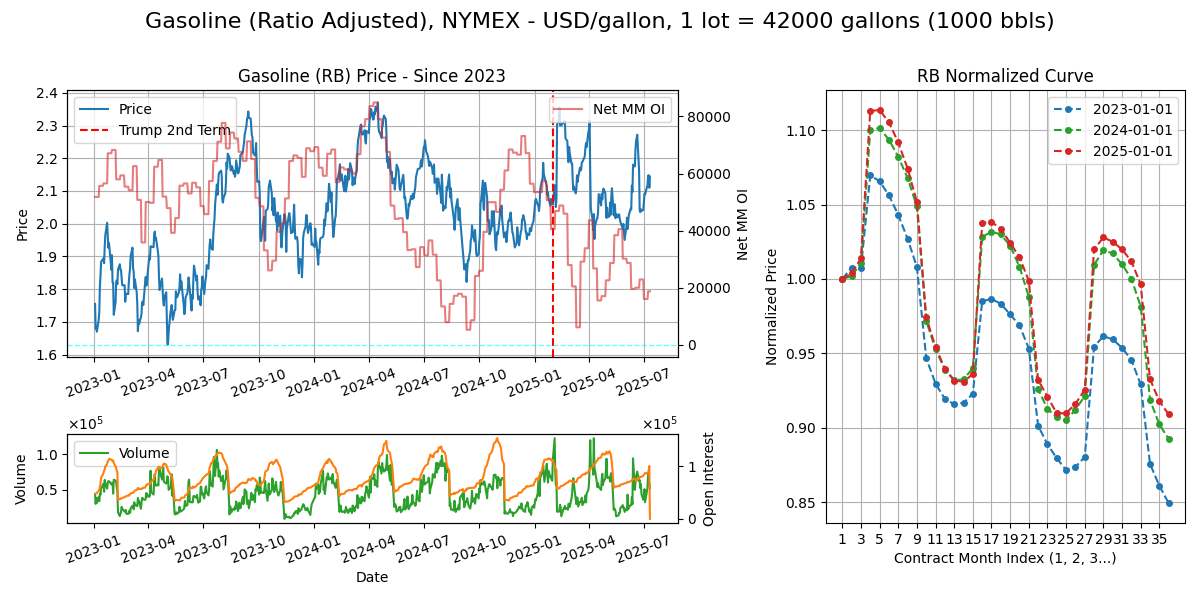
Calendar - 3Y ahead monthly contracts. Trading stops last BD of M-1. Weekdays except 11pm-12am GMT.
Specs - Gasoline is interesting - Blending is complex and any gasoline spec is a carefully blended cocktail rather homogenous liquid with winter/summer blends (vapor pressure diff). BOB = blendstock for oxygenate blending, mixed with ethanol (oxygenate) at terminal (avoid water contamination), loaded into tanker trucks, delivered to gas station/pump.
Curve Structure - Demand/driving aside, on supply, lowering vapor pressure by extracting easily vaporized compounds (like butane) requires a cost.
Supply Chain
Export/Import: Export: SGC (35%), EU (20%), Asia (20%), ME (10%), rest. Import: Latam (35%), USEC (15%), WAF (15%), SEA (15%), rest.
Gas
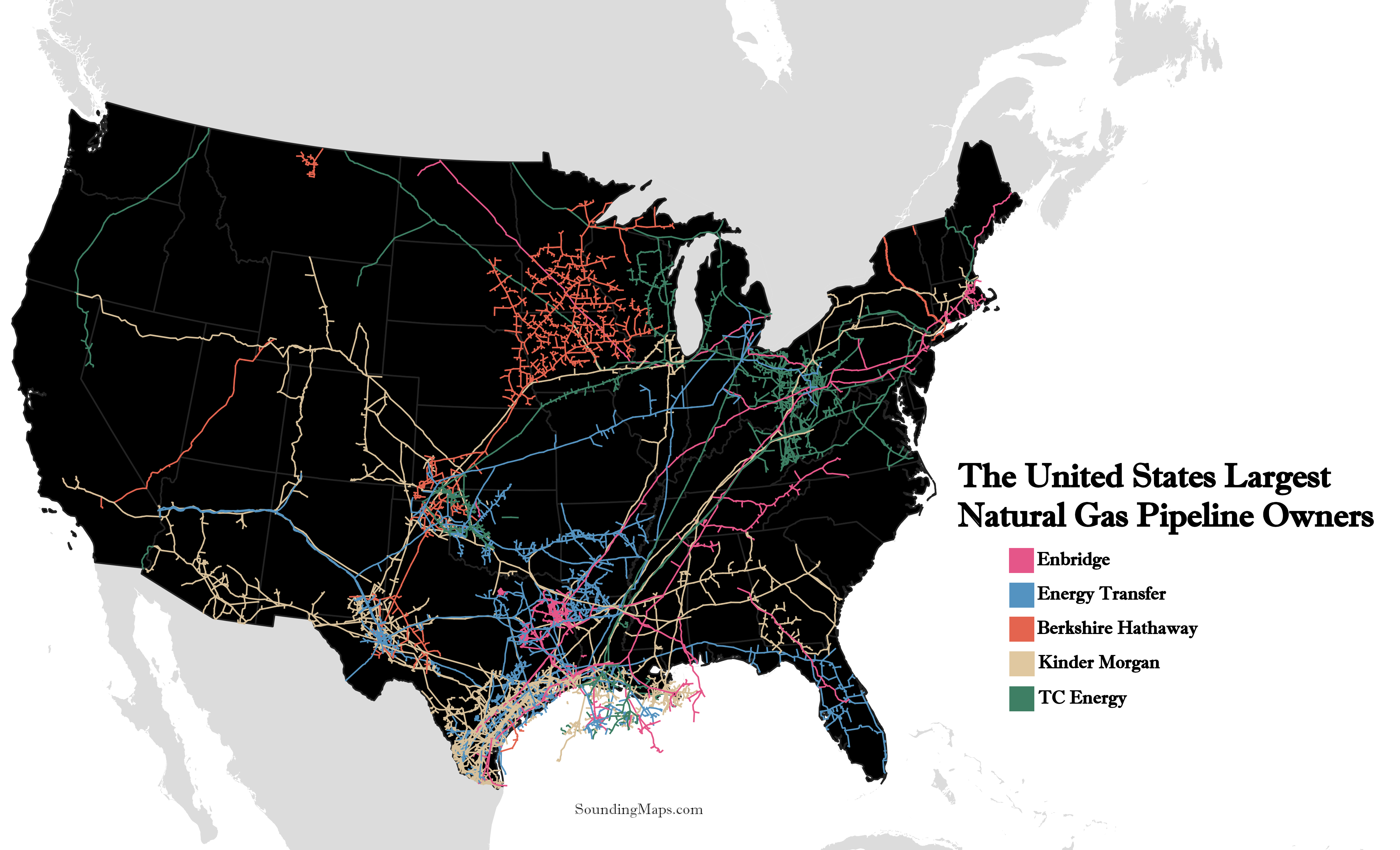
Henry Hub (NG)
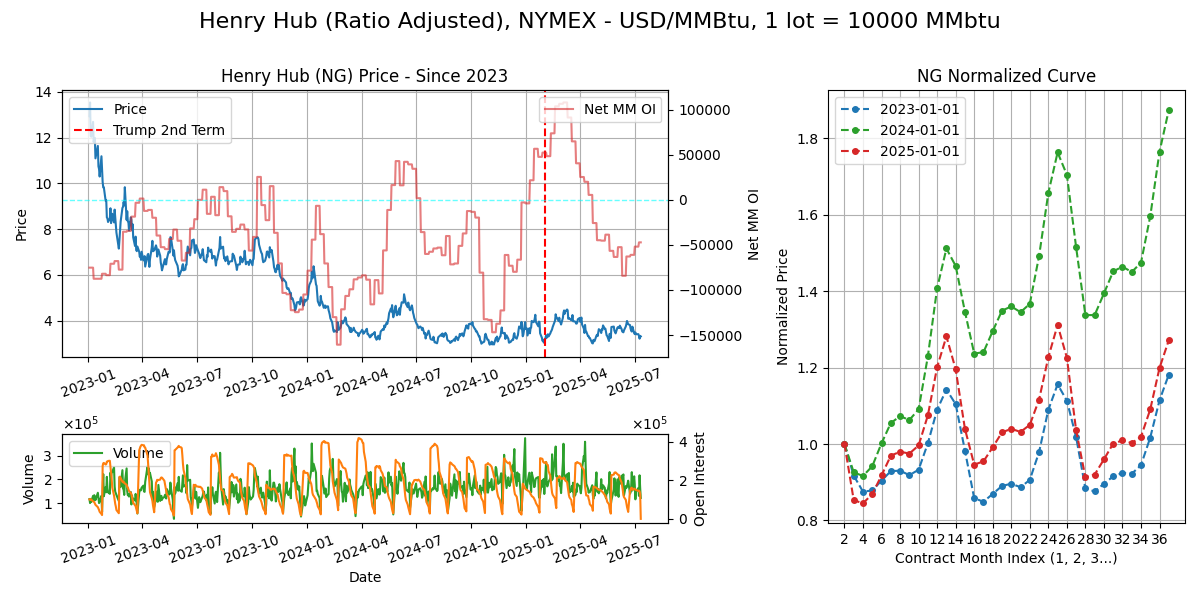
Calendar - 12Y ahead, monthly contracts. Expires 3rd last BD of M-1. Weekdays except 11pm-12am GMT.
Delivery - Via pipeline network at Henry Hub Louisiana. 1 lot of gas uniformly delivered across delivery month.
Curve Structure - Nat gas exhibits the strongest seasonality of all the futures curves here, with a strong winter premium for restocking of gas storages for the winter period.
Supply Chain
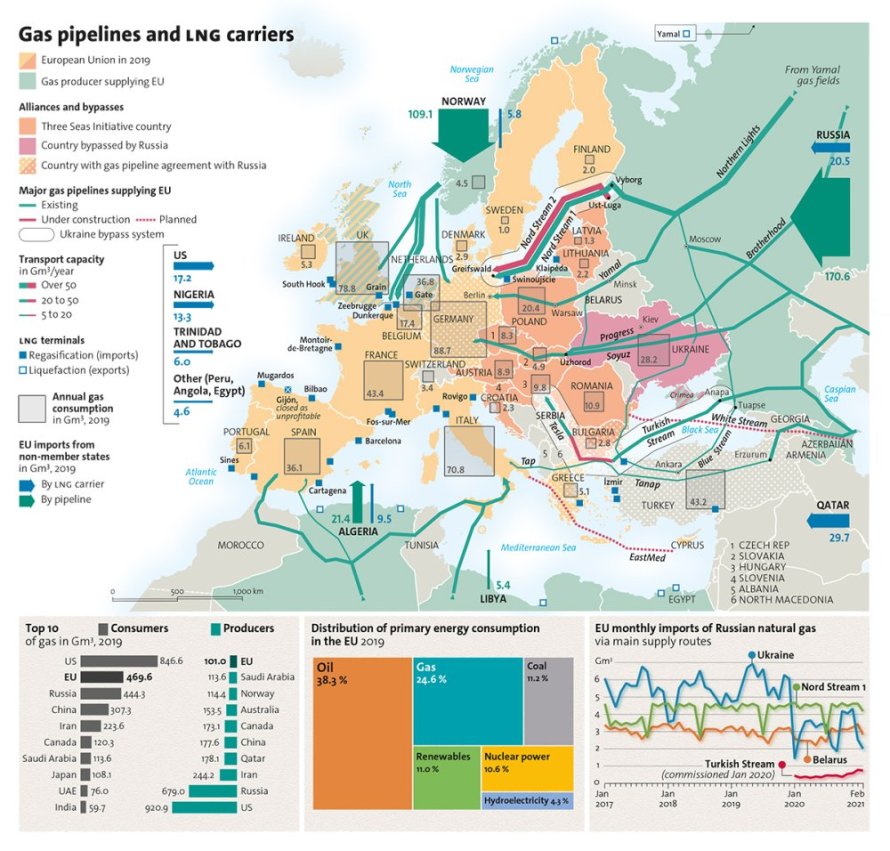
Export/Import - Export: US (20%), Russia (10%), Norway (10%), Qatar (10%), Aus (10%), Canada (5%), Algeria (5%). Import: EU, Asia, RoW
Use Case: Powerburn (40%), rescomm heating/LDC (20%) industrial - feedstock (30%). For feedstock: industrial fuel, hydrogen (steam-methane reforming CH4 + H20 > CO + 3H2, hydrogen then used for hydrocracking/hydrodesulfurization, or ammonia creation via Haber Bosch N2 + 3H2 > 2NH3, then fertilizer).
Seasons - Hurricane season (June-Nov), winter (Nov-Mar)
TTF (No data)
Calendar - 13Y ahead, monthly contracts. Expires BD prior to first gas day of delivery month. Weekdays 7am-5pm GMT.
Delivery - Transfer of rights at TTF Virtual Trading Point operated by Gasunie. “Delivery made equally each hour through delivery month”.
Products - Many products depending on settlement type, tenor, etc. TFM (TTF monthly futures, physical EUR/MWH), TFU (1st line futures, financial, settles to 1st line index, USD/MMBTU), TTL (daily financial futures, 92D ahead), TFE (daily physical futures, 92D ahead). IFEU and Endex.
Curve Structure - Gas balance peaks in Oct and draws down till April as spring enters.
Pricing - Euro/MWH, 1 lot = 1MWh gas delivered hourly over contract month (700h) so 700MWH over month. If one household is 0.3MWH/month at 30% average hourly mix of electricity = 2100 households per lot.
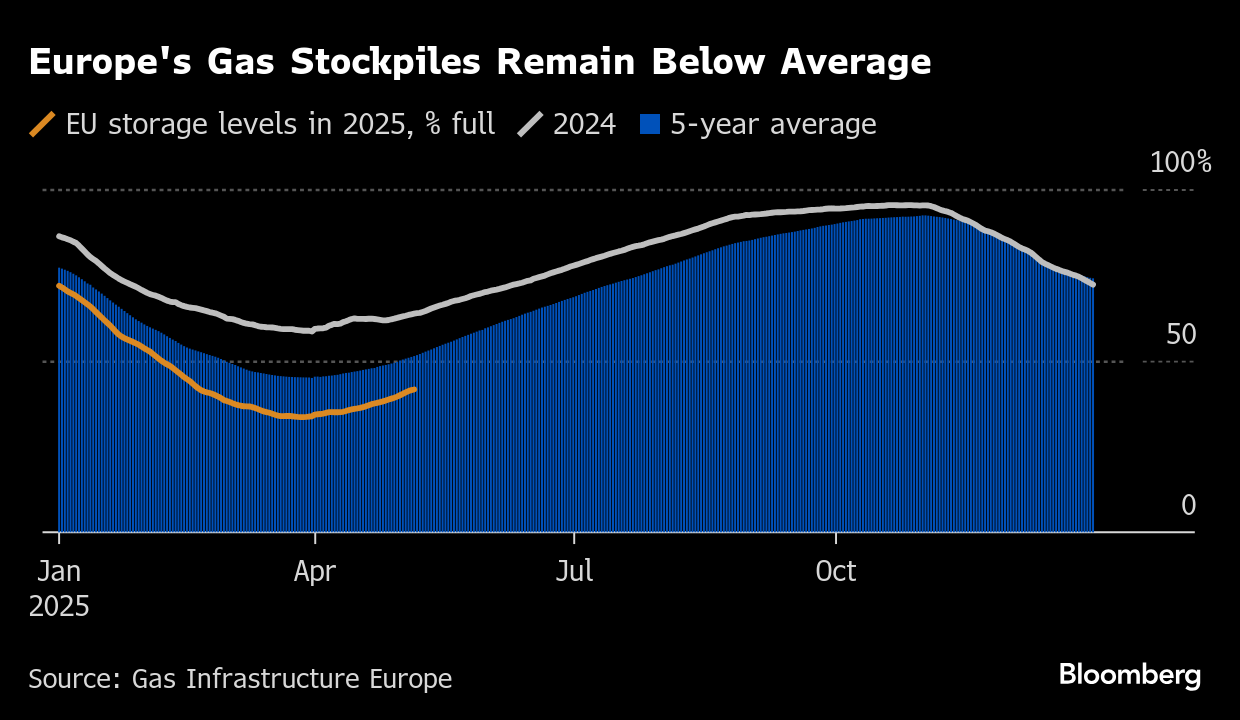
Storage Cycle - In non-winter (spring > summer > autumn), supply > demand = storage builds, in winter months (Nov Dec Jan Feb Mar), demand > supply = storage draws then begins to refill, yearly seasonal cycle.
LNG Flow - Project structure very complex, flow under very complex long term SPAs (e.g 10Y, 20Y agreements) 80% and remainder spot cargoes depending on the arbs/econs.
Numeracy - Qmax = 260k CM (0.5 CBM to MT) = 130k T. Russian exports of LNG to EU in 2024 = 15 MT = 100 Qmax. Russian pipeline gas exports to EU in 2024 = 32b CM = 23 MT (1BCM = 0.73 MT)
Power
Calendar
More confusing. Power futures have different tenors, listed for advance time periods. Longer tenor = longer curve out. Series of overlapping curves.
Contracts are listed in an advance window. Again, longer tenors = longer advance window. Cascading (breaking of contract in delivery into smaller tenor contracts) can happen due to overlapping delivery periods which affects MTM.
Supply Chain
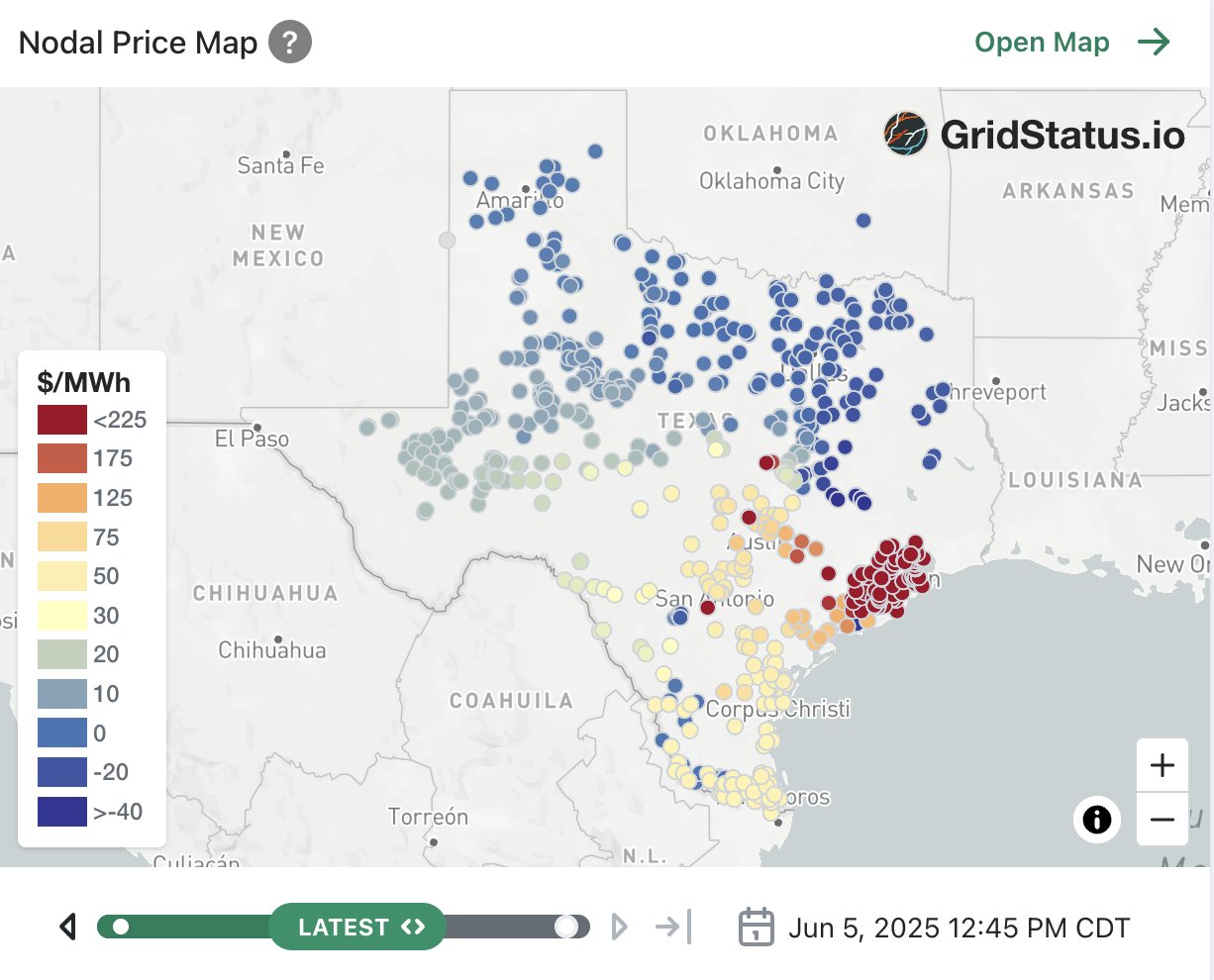
Markets - Nodal vs zonal. Determined by massive LP solvers and centralized, sealed bid uniform clearing auctions to maximize total welfare (producer + consumer surplus) across MTU. Ensure S==D constantly as much as possible. Retailers pay wholesalers/producers and end customers pay retailers. Any secondary player does cash swapping in a chain/network.
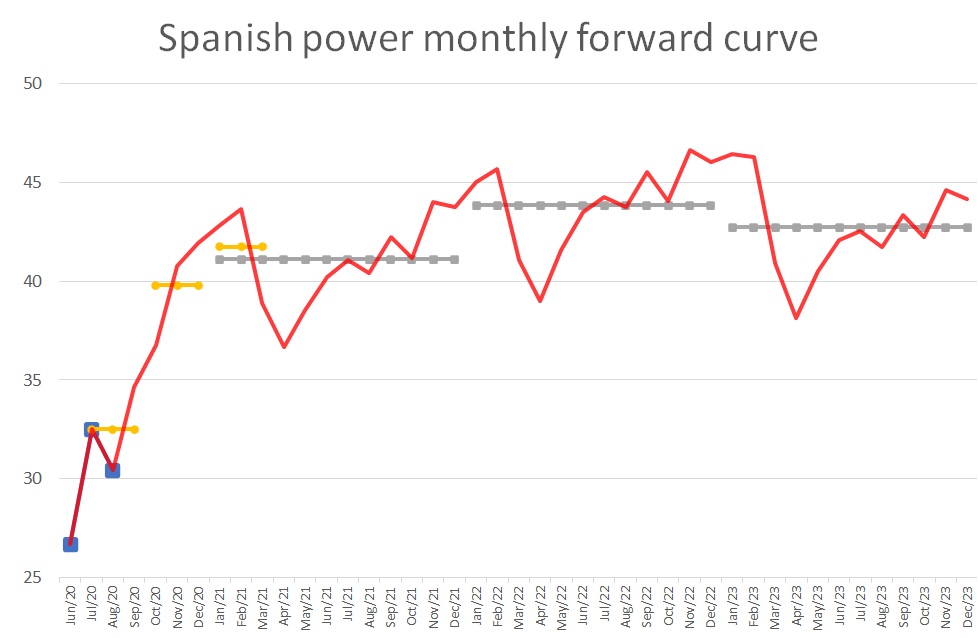
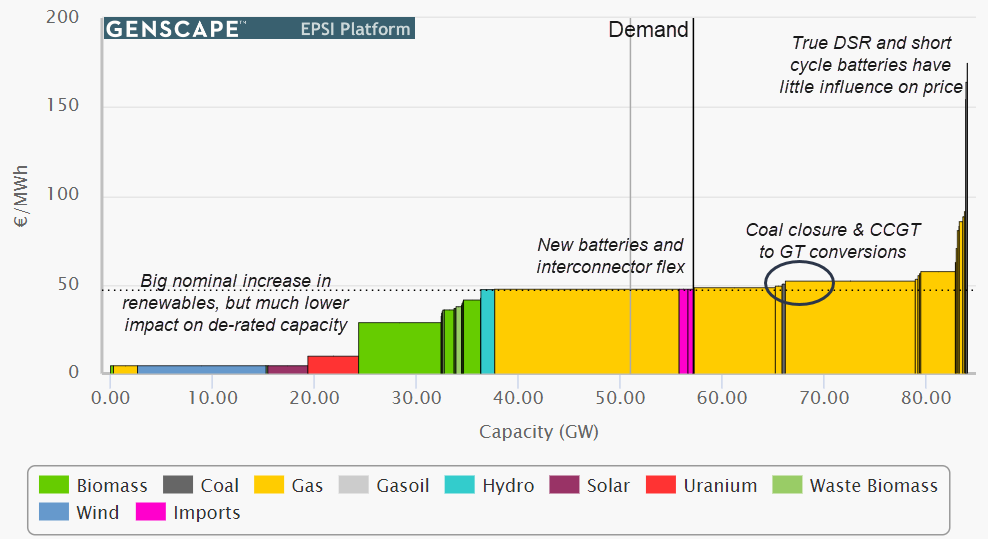
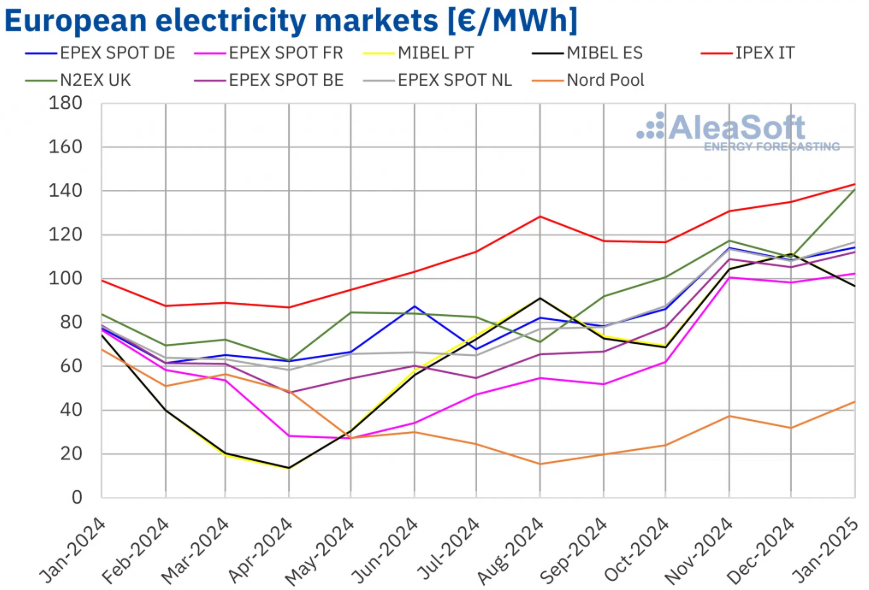
O&G-Adjacent: Fertilizers/Ammonia
Supply Chain
- Plants - Located near refineries + natgas facilities.
- Import/Export - Export: China (15%), Canada (15%), EU (10%), US (10%), Morocco (10%), etc. Import: Brazil (20%), India (12%), US (12%), EU (10%).
- Process - Nitrogen, phosphate (Morocco, China, etc) , potassium/potash (Canada, Russia, etc), sulfur + ammonia synthesis = fertilizer.
Metals/Dry
Copper (HG)
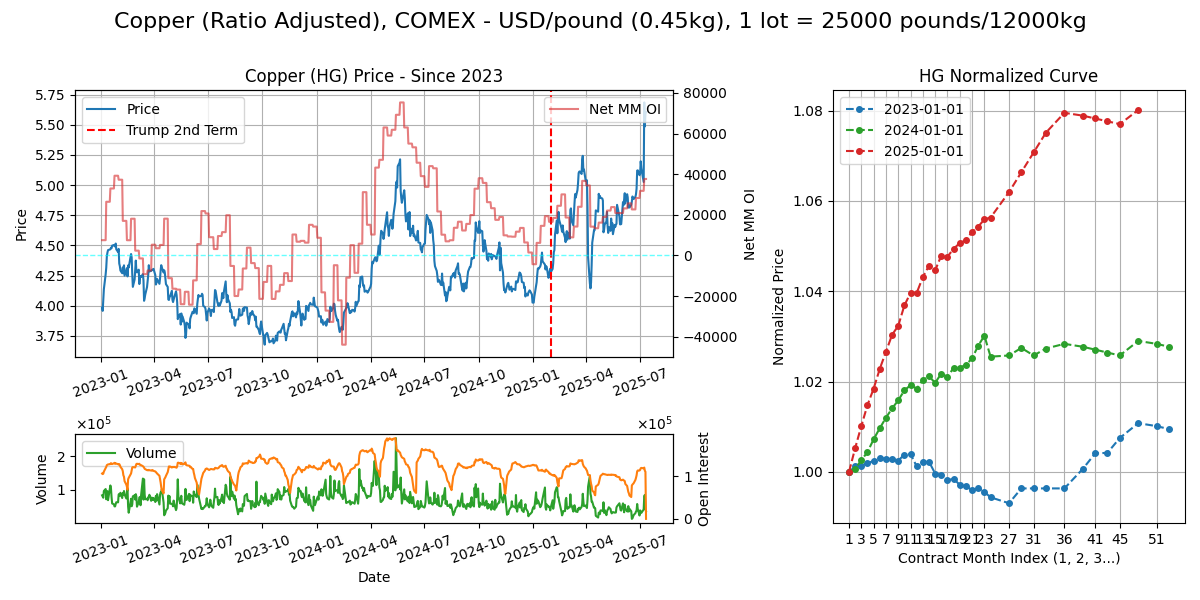
Calendar - 2Y monthly then sparser 5Y out. Weekdays except 11pm-12am GMT.
Delivery - Delivery of cathode to CME exchange licensed warehouses (country-wide) with warrant. Worth noting COMEX, LME, SHFE are the main 3. Concentrate goes in bulkers, cathode in containers.
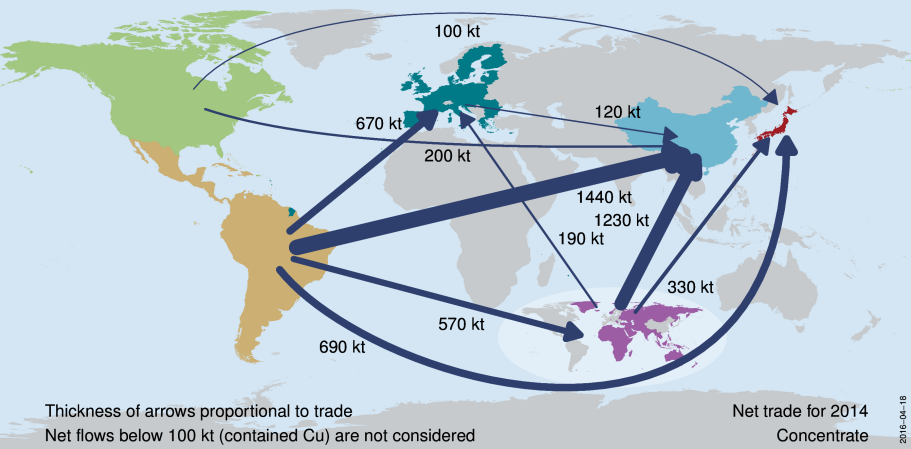
Supply Chain
Processing - Ore (brownish rock) > chemical treatment to concentrate (greenish rock) > treatment/smelting cost (TC) to blister copper > refining cost (RC) to pure copper cathode.
Export/Import (Ore/Concentrate) - Exporters: Chile (30%), Peru (25%), Indonesia (10%), Australia (5%), Importers: China (65%), Japan (15%), rest. Chinese have huge smelting capacity.
Use Case - Buildings/construction - wirings, plumbing (40%), grid infrastructure - transformers, lines, substations, etc (20%), industrial machinery (20%), transportation - wiring (20%). Many conflicting sources..
Routes - Handy and Supramax, Chile (Antofagasta) to China (Yangshan, Qingdao, Shanghai)
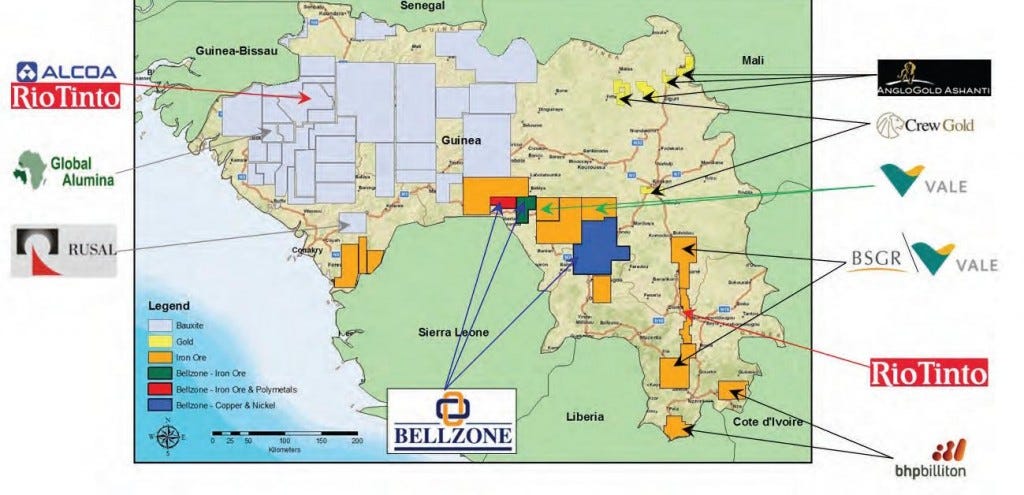
Aluminium (ALI)
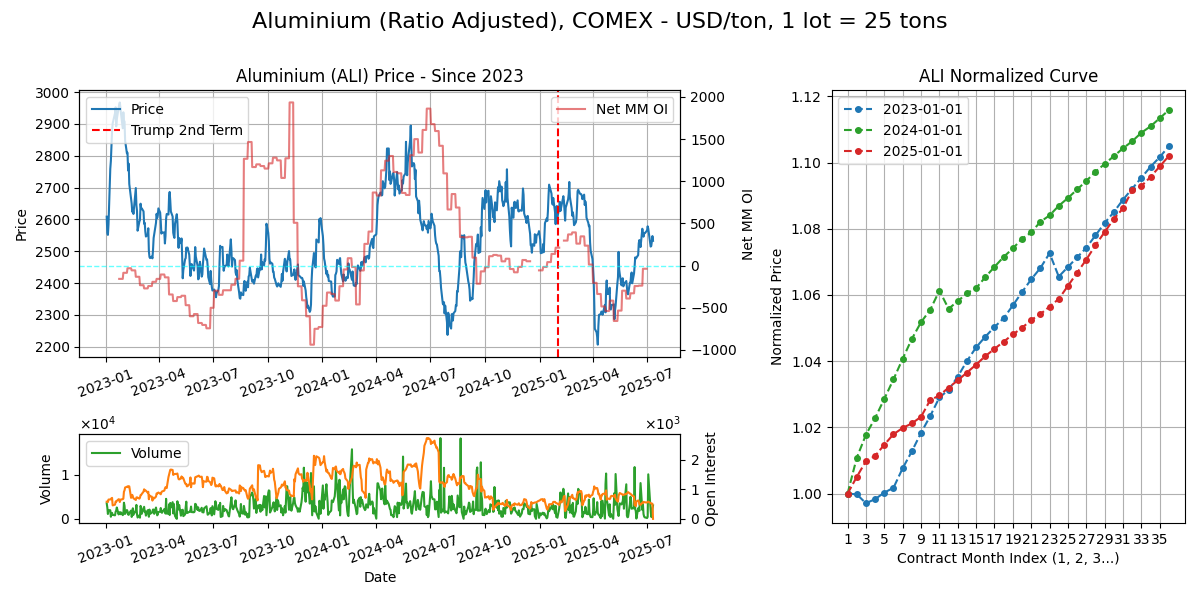
Calendar - 5Y monthly, LTD is 3rd last BD of the month. Weekdays except 11pm-12am GMT.
Delivery - Delivery of ingots to US, EU (Antwerp, Bilbao, Rotterdam) and APAC (Johor, Port Klang, SG, Busan) COMEX warehouses
Supply Chain
Export/Import (Bauxite) - Exporters: Guinea (60%), Australia (15%), Brazil (10%), Indonesia (5%). Importers: China (85%) again with massive electro-refining capacity, EU (5%)
Use Case - Transportation vehicles - airplanes are 80% aluminium by weight, car chassis, etc (30%), construction (25%), packaging (20%), electronics (15%)
Routes - Panamax/Kamsarmax (80kt), Guinea (Conakry), Australia (Port Hedland) to China (Shanghai).
Steel (HRC)
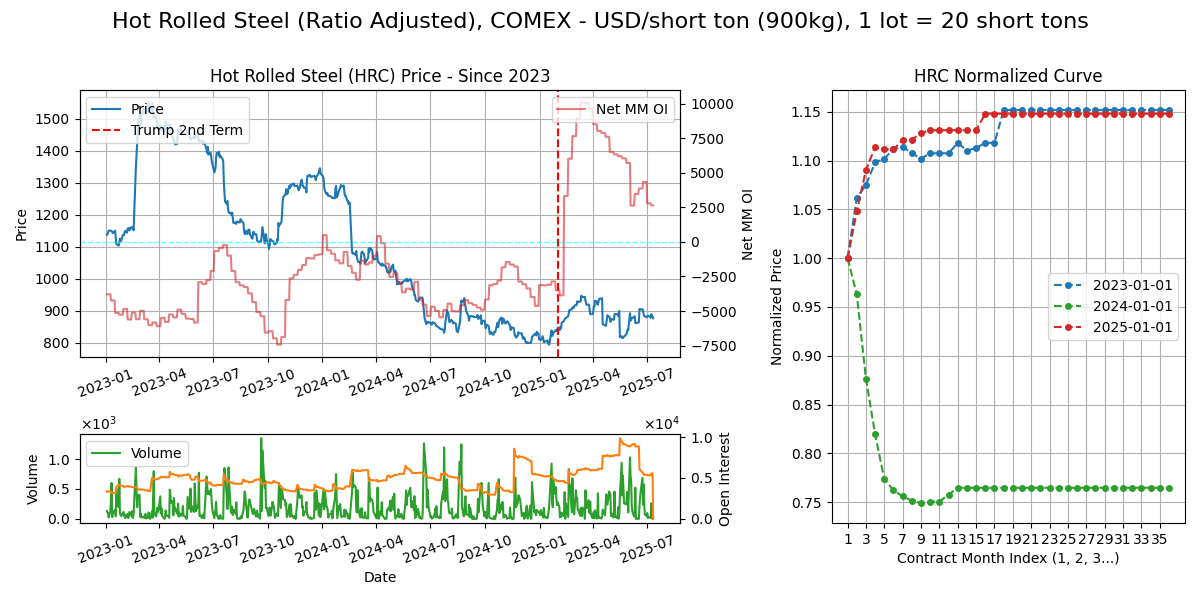
Calendar - 3Y out monthly, trading terminates BD prior to last Wed of M. Hardly traded. Liquidity elsewhere? Weekdays except 11pm-12am GMT.
Specs - US Midwest domestic hot-rolled steel coils. Financially settled. Large range of steel products: flat (coils), long (rebar).
Supply Chain
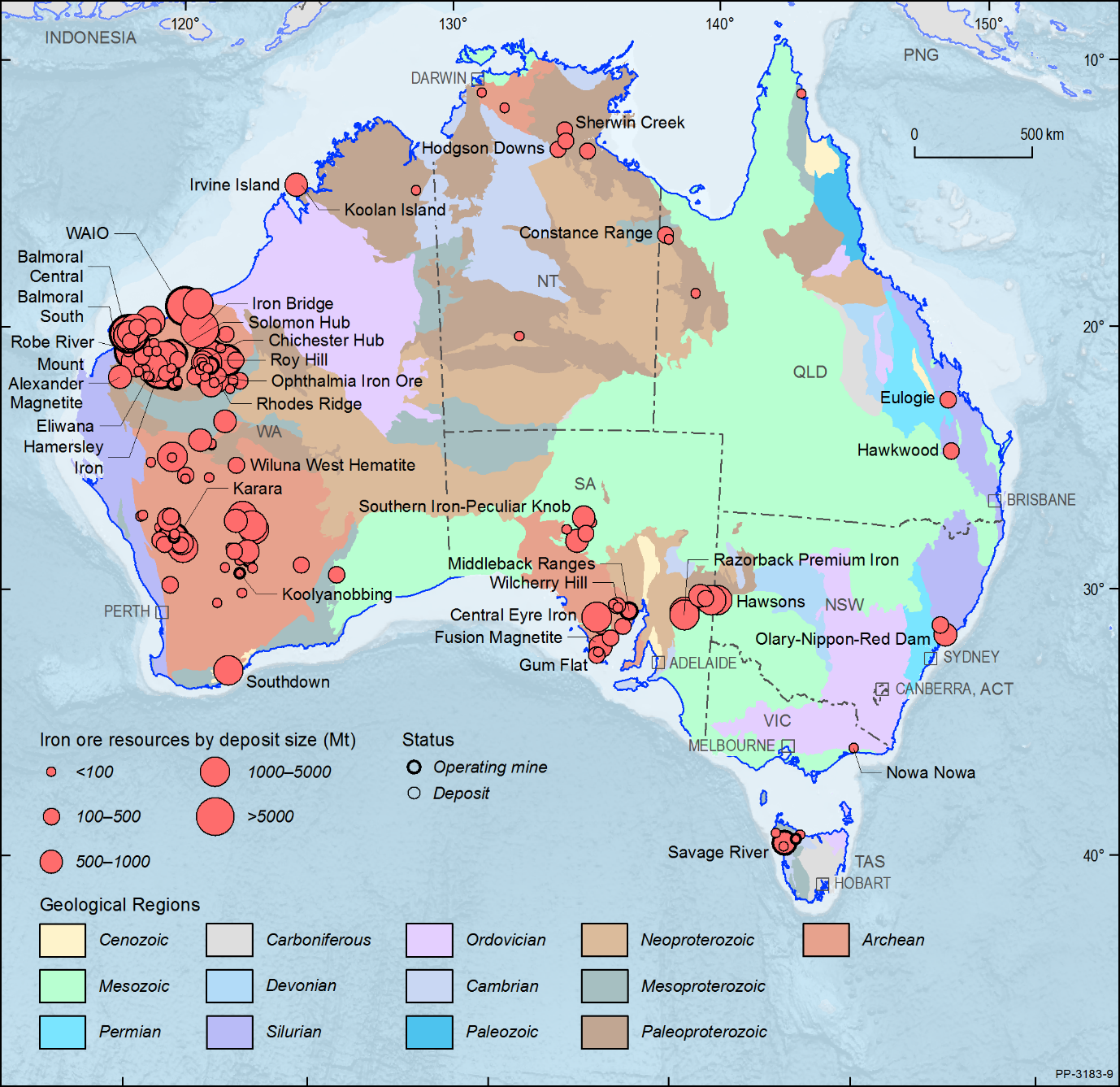
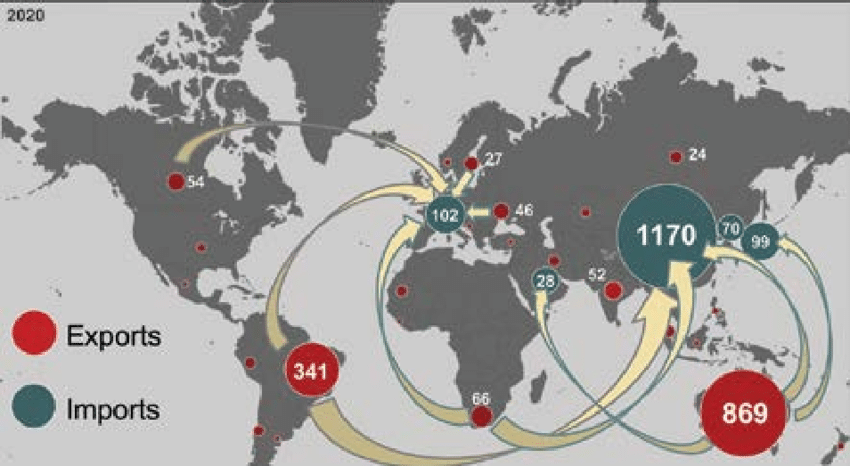
Exports/Imports (Iron Ore) - Exporters: Australia (50%), Brazil (20%), Canada (5%), SA (5%), etc. Importers: China (70%), Japan (10%), SK (10%), etc.
Exports/Imports (Steel) - Exporters: China (25%), Japan (7%), SK (6%), Germany (5%), etc. Importers: China (8%), USA (8%), Germany (7%), Italy (6%), Turkey (5%). Diff product type.
Iron Ore - Hematite (lower iron content) and magnetite (higher iron content). Hematite found in Australia, Brazil, China, magnetite found in US, Canada, etc
Steelmaking - Pure iron is very soft and ductile. Steel is higher in strength and hardness, an alloy of iron with carbon (C) and other alloying elements (Mn, Cr, Ni, Mo, V etc). Carbon changes lattice structure. Good for applications where hardness/strength needed (e.g ship hulls cannot collapse under weight of cargo). Made via BOF (blast furnace/basic oxygen furnace) - pet coke / met coal burned, generates CO2, carbon from coke dissolves into molten iron = steel. Oxygen O2 is blown, oxidize excess carbon to 0.02 to 2%. Reduce Fe203 to Fe then add some carbon. Electric arc furnace (EAF): melt scrap steel, inject carbon (coke, carbon powder) into melt.
Use Case - Construction (buildings, infrastructure) (50%), mechanical equipment (15%), automotive/cars (10%), other transport like ships (5%).
Routes - Capesize (120-200 kt), Valemax (380-400kt), Brazil (Tubarao), Australia (Port Hedland/Dampier) to China (Qingdao).
Seasonality - Steel inventory peaks in China in Spring as in cold winter/post LNY construction slows but production continues.

Coal (NCF)
Calendar - 84 consecutive month contracts (7Y out). Weekdays 1am-11pm GMT. LTD on last Friday of M.
Specs/Delivery - 1 lot = 1000 tonnes of thermal coal, ICE/IFEU. Financially settled based on loaded coal FOB at Newcastle Coal Terminal (NSW, East Coast, North of Sydney) in Australia. Settled on globalCOAL (owned by consortium of coal trading shareholders) monthly NEWC index. Also have Rotterdam and Richards Bay coal futures.
Supply Chain
Use Case - Power gen - thermal (70%), steel/metallurgy - coking (20%). Coking/anthracite coal = higher carbon content (80/90%), higher calorific/heat value, premium to thermal. Used in steelmaking/blast furnaces. Within thermal, black/bituminous and brown/lignite (50-70%). Name from max temp/pressure geologic conditions under coalification.
Exports/Imports - Exports: Indonesia (35%), Australia (30%), Russia (15%), US (5%), SA (5%), Colombia (5%) etc. Imports: China (25%), India (20%), Japan (15%), SK (10%), EU (10%), SEA (8%), Taiwan (5%)
Freight/FFAs
Specs/Delivery
Trading/Daily Settlement - OTC/brokers. Whatsapp chats, voice brokers, broker screens (updated manually by brokers, not executable). Once cleared/filled, broker sends trade to clearer (exchange) who settles the price and publishes for MTM daily at closing time. Daily settle, no intraday OHLC/bars.
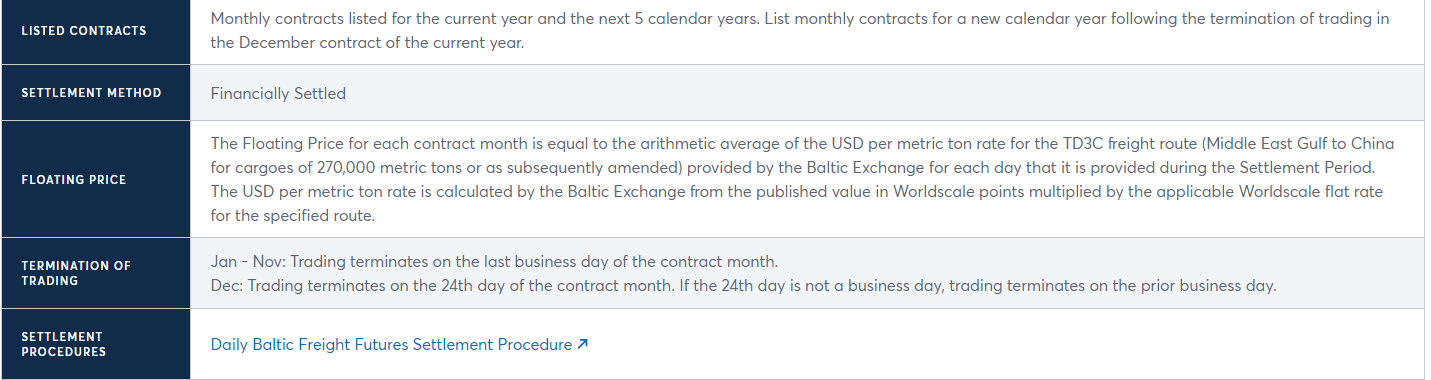
Delivery - Trading/MTM/margining happens in delivery month but final settlement after delivery month against monthly average of a voyage/time charter index/route (e.g TD3C MEG to Japan)
Indexes - Freight rates or indices published daily by Baltic Exchange (main freight PRA), derived from spot transactions reported by shipbrokers (Clarksons, Braemar, Gibson etc). Index = weighted basket of freight routes under standardized conditions (vessel, route, cargo: fuel cost, port charges, canal fees, speed, laytime schedules etc). WS100 = standardized flat rate in %, published yearly, of $/t. Shipowners negotiate rates with reference to % of worldscale then convert to dollar/ton basis.
Exchanges/Products
SGX - Dry bulk, tankers, containers, LNG/LPG.
ICE - Select tankers/gas FFAs.
Grains
Concepts
- Supply = Carry in + domestic production (yield * acreage) + imports - exports
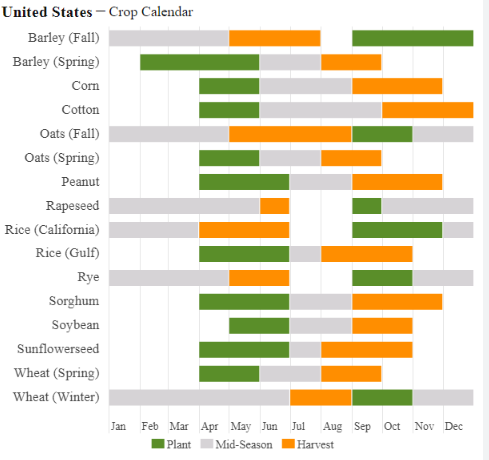
- General Crop Cycle = Planting > Growing > Harvest > Storage/Marketing
- Single Year Crops - Corn, soybeans, wheat, rice, cotton, sorghum, barley, sunflowers, peanuts
- Multi-Year Crops - Coffee (2-4), cocoa (3-5), sugarcane, sugar beet
- Climate - Tropical: coffee, cocoa, rice, sugarcane. Subtropical: soybean. Temperate: wheat, barley, oats, soybean, canola, sugar beet.
- Futures - Mostly at 2M odd intervals + an Oct/Nov/Dec contract.
Corn (ZC)
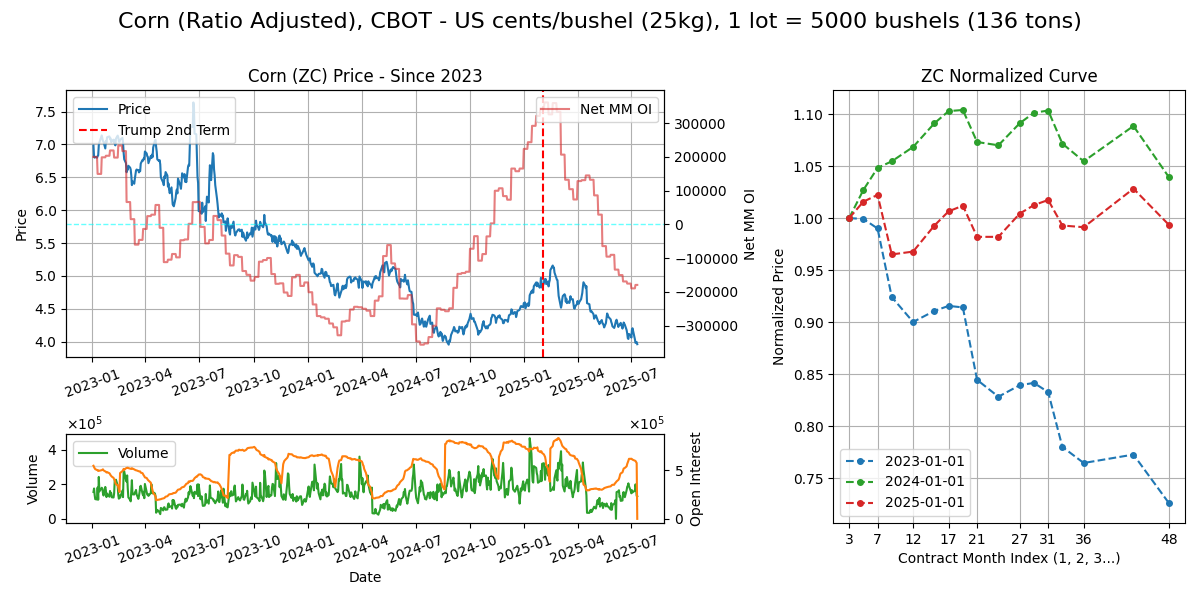
Calendar - 3Y out, but contracts deliver in 3,5,7,9,12. trading terminates BD prior to 15th of M, Weekdays 8.30am-1.20pm CT or 2.30pm-7.20pm London.
Specs - CBOT Rulebook. No. 1/2/3 kernel grade at discount premium. The kernel is the seedbearing part of the fruit/ears.
Delivery - US corn belt farm (midwest - Indiana, Iowa, Michigan, etc) > elevators > truck, rail and barge > various warehouses at delivery ports which are along the Mississipi river system, down to US Gulf for export > bulker.
Supply Chain
Climate - 18-25c in growing season.
Use Cases - feedgrain (35%), blending ethanol (35%), FSI at 15%, and surplus exports (15%).
Major Export/Import/Swing Countries - Exporters: US (35%), Brazil (30%), Argentina (20%), Ukraine (15%). Importers: Mexico (13%), Japan (10%), EU (10%), SK (6%), China (6%). Quite balanced. Countries that have livestock farming but no crop?
Crop Calendar/Cycle - US: Planting (Spring months: Apr/May), growing/silking (Jun, Jul, Aug), harvest (Sep, Oct, Nov), while Brazil has a unique two corn crop cycle due to climate variation.
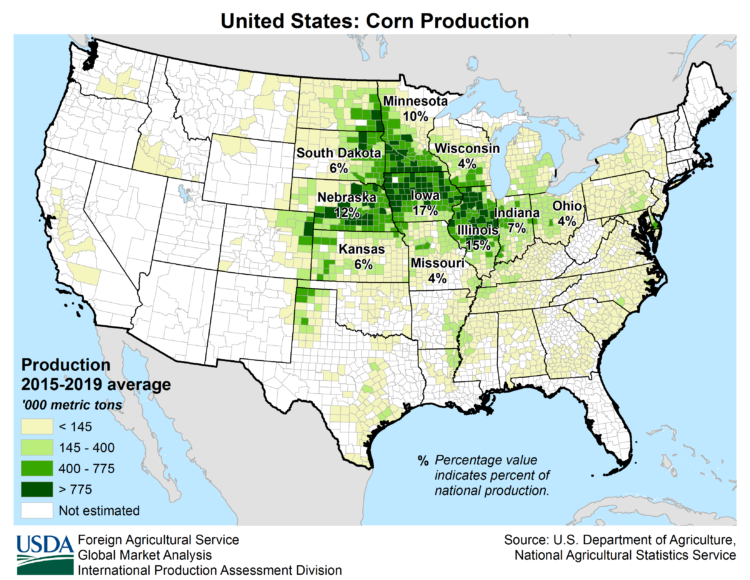
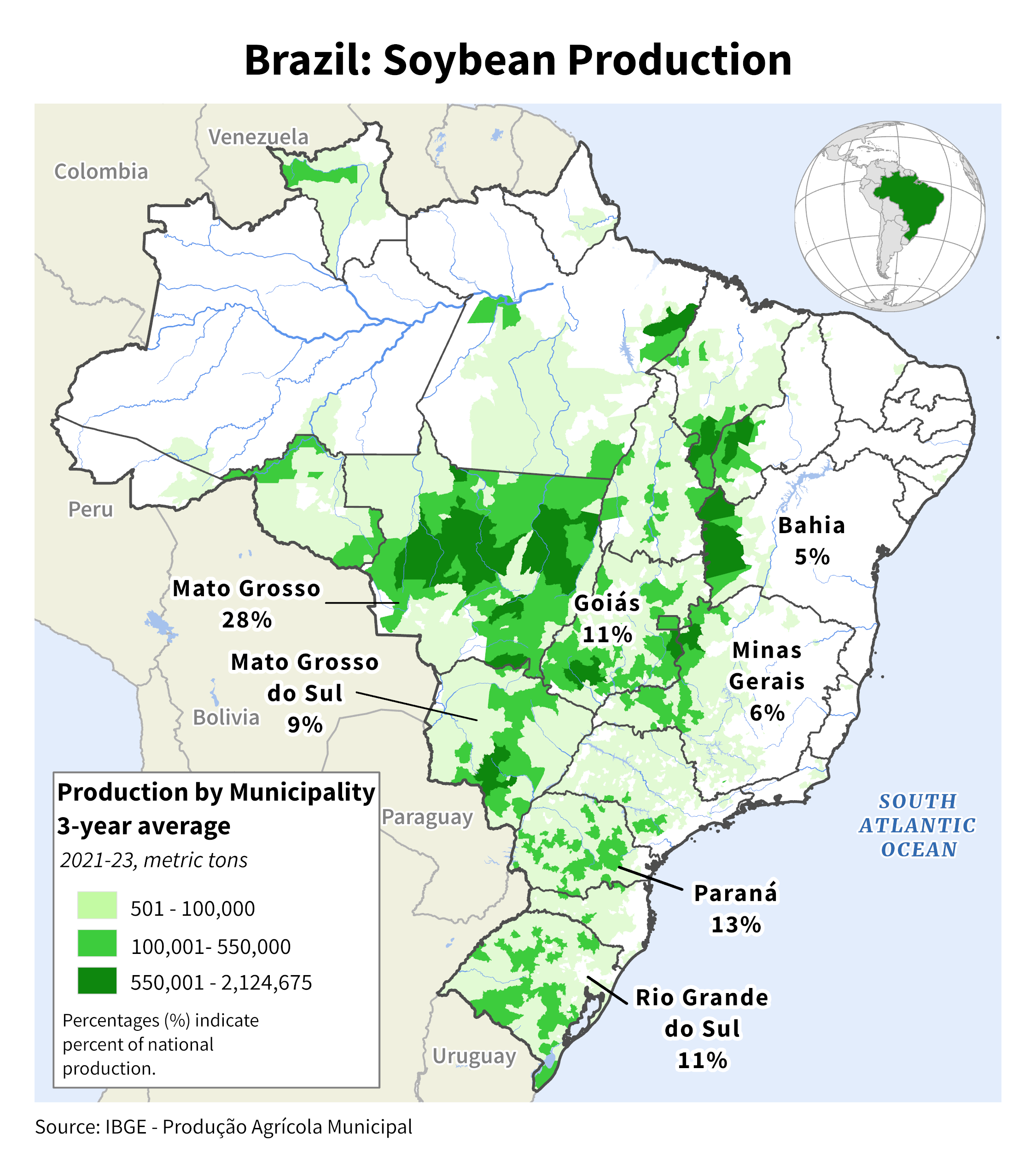
Soybeans (ZS)
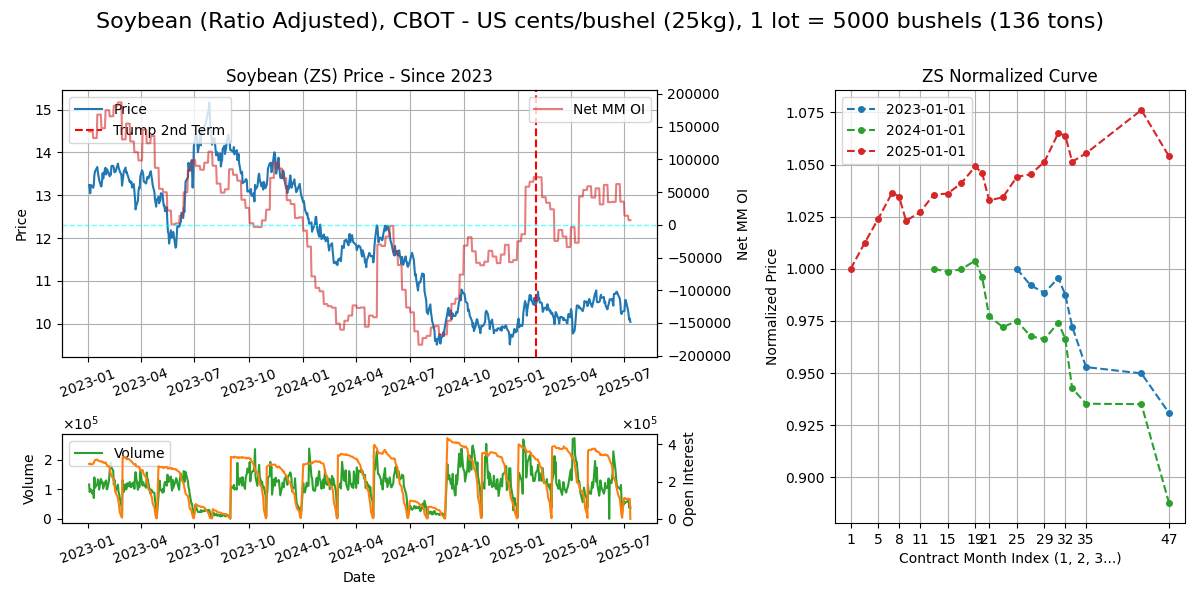
Calendar - 4Y out, 1,3,5,7,8,9,11. Incomplete data from FRD but the same June/July premium exists like corn (old crop). Weekdays 8.30am-1.20pm CT or 2.30pm-7.20pm London.
Delivery - Similar warehouses along the Mississipi river system, as the Soybean belt is similar to the corn belt.
Supply Chain
Climate - 20-35c in growing season. Prefers warmer temps.
Use Cases - Crushing (85%) to oil and meal, FSI (10%). 80% meal 20% oil. Meal goes to animal feed (feed mills/livestock farmers), oil goes to cooking (food processors) and biofuels (fuel producers).
Major Export/Import/Swing Countries - Exporters: Brazil (60%), US (30%), Paraguay (5%), Argentina (5%). Importers: China (66%), EU (10%), Mexico (5%), Thailand (2%) etc.
Crop Calendar/Cycle - US: corn but shifted 2M forward (to get summer temps), Brazil: Planting (summer: Nov/Dec), growing (Jan/Feb), harvest (autumn: Mar-Jun)
SRW Wheat (ZW)
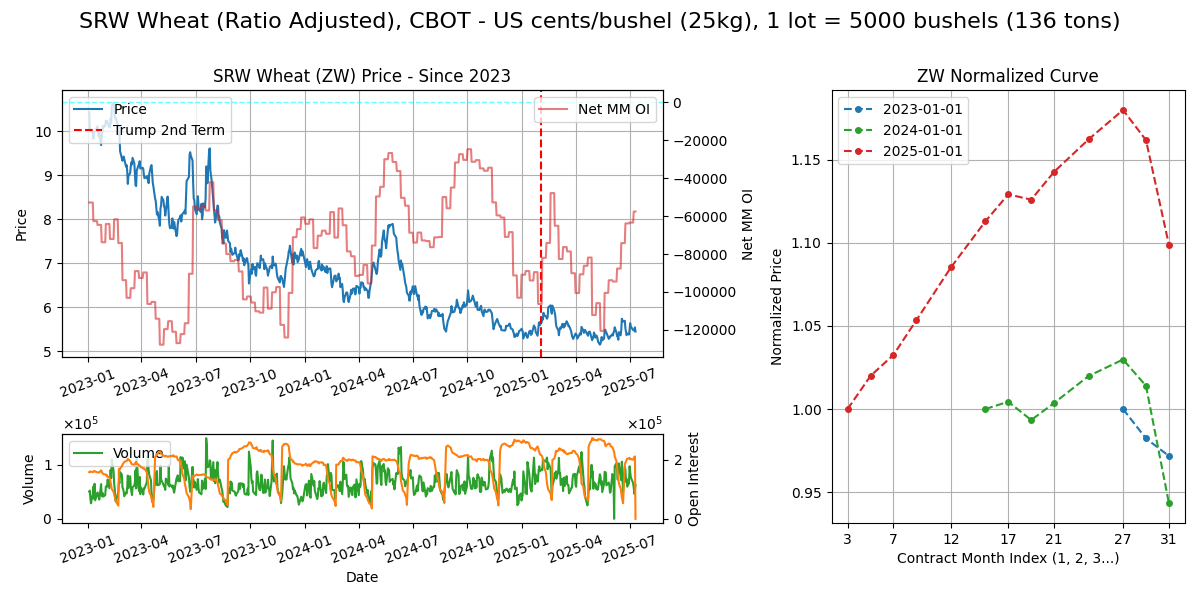
Calendar - 3Y out, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12. Terminates BD prior to 15th of M. Weekdays 8.30am-1.20pm CT or 2.30pm-7.20pm London
Delivery - CME offers Chicago SRW, KC HRW, and Black Sea Wheat futures, with first one being most traded. Assume delivery is similar to Corn/Soybean.
Supply Chain
Climate - Spring wheat: 20-25c, winter wheat vernalises at 5-15c. Spring wheat grown in Northern Great Plains (Dakota, Montana etc) - winterkill too cold for winter wheat, winter wheat in central states (Kansas).
Curve Structure - Slight premium at May contract, presumably due to last of old crop before next harvest.
Use Case: Unlike Soybean and Corn, majority (75%) to FSI. Hard wheat (high protein) = bread/pasta, soft wheat (low protein) = cakes/pastries.
Major Export/Import/Swing Countries: Exporters: Russia (20%), EU (15%), Canada (15%), Australia (10%), US (10%), Ukraine (10%). Importers: Very spread out. Everyone needs wheat for food.
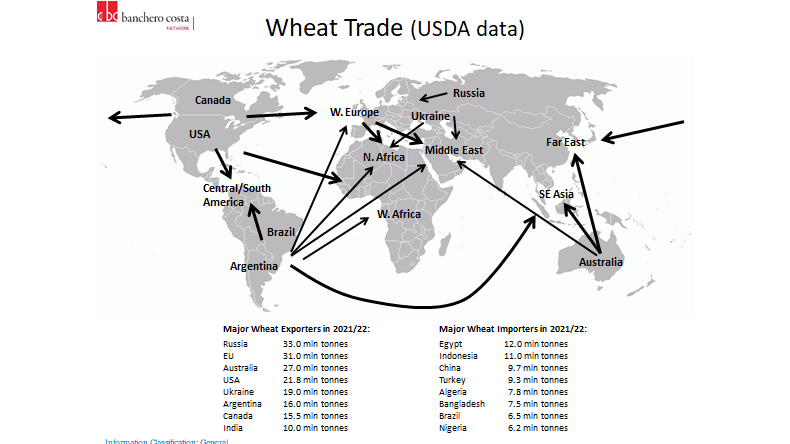
Rough Rice (ZR)
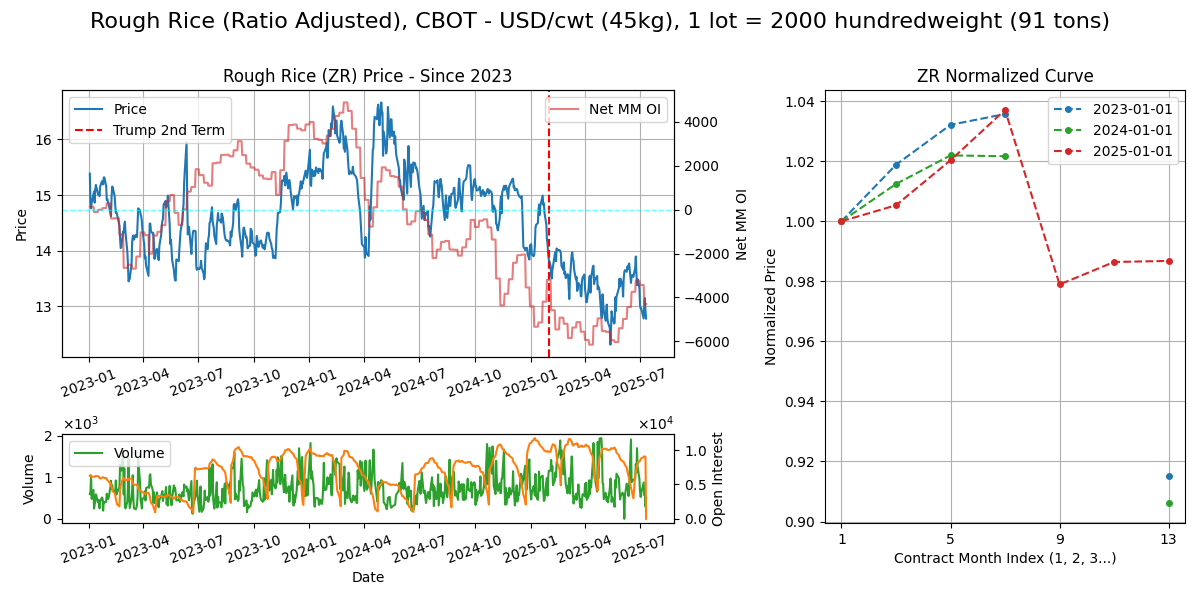
Calendar - 1Y out, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 Terminates BD prior to 15th of M. Weekdays 8.30am-1.20pm CT or 2.30pm-7.20pm London
Delivery - Deliveries of rough rice shall be made only by delivery of rough rice shipping certificates issued by warehouses located in the Arkansas counties of etc. Chinese rice futures on DCE (Dalian).
Supply Chain
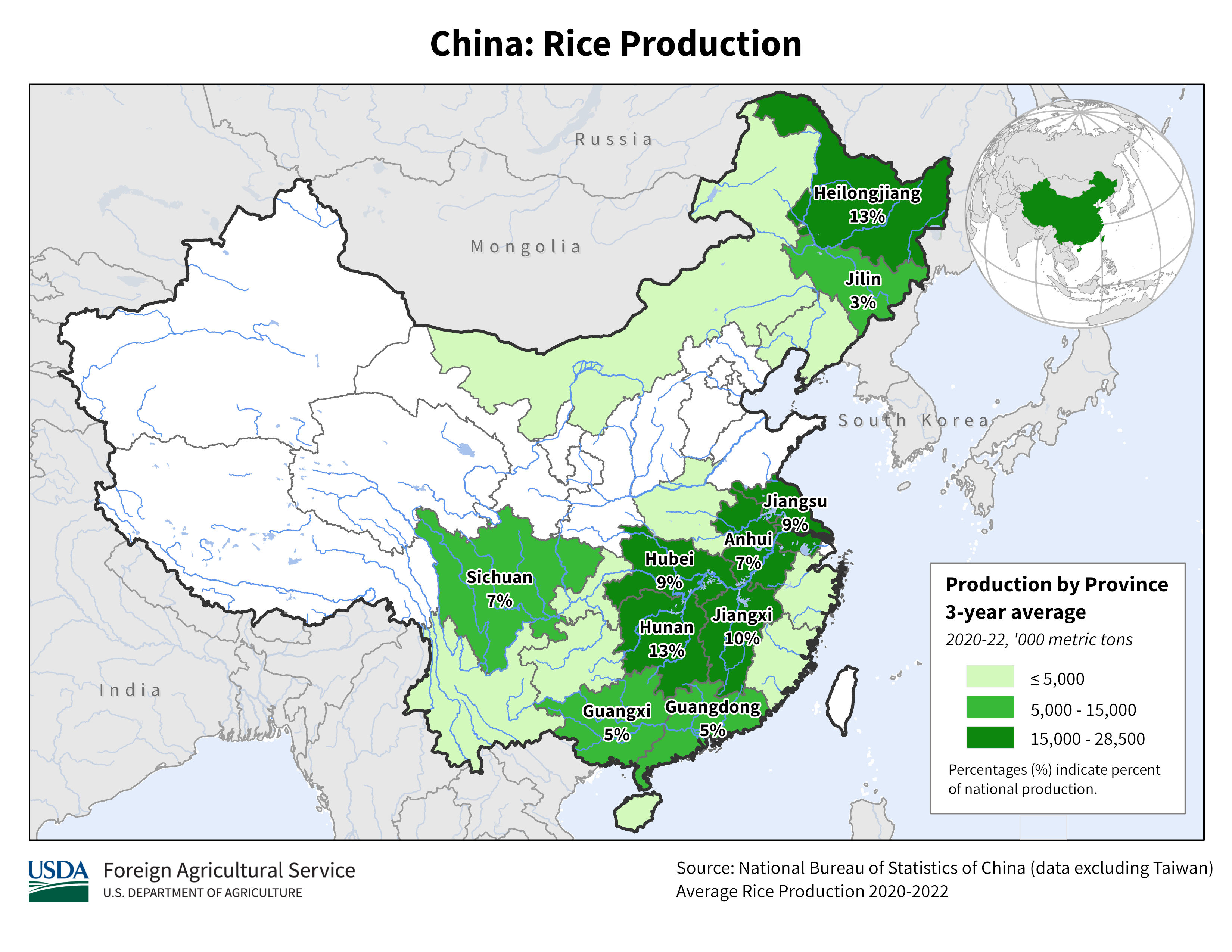
Climate - Rice grows in hot wet climates, in US, Arkansas is most suited (45% of US rice prod). China & India dominate. Within China, from USDA map, NE in Heilongjiang and another belt in the South.
Crop Cycle - Seed to harvest in 6 months. Feb to Nov in China. Early rice and late rice / double season rice.
Use Case - Majority FSI and majority in Asian countries as the staple of course.
Softs
Cocoa (CC)
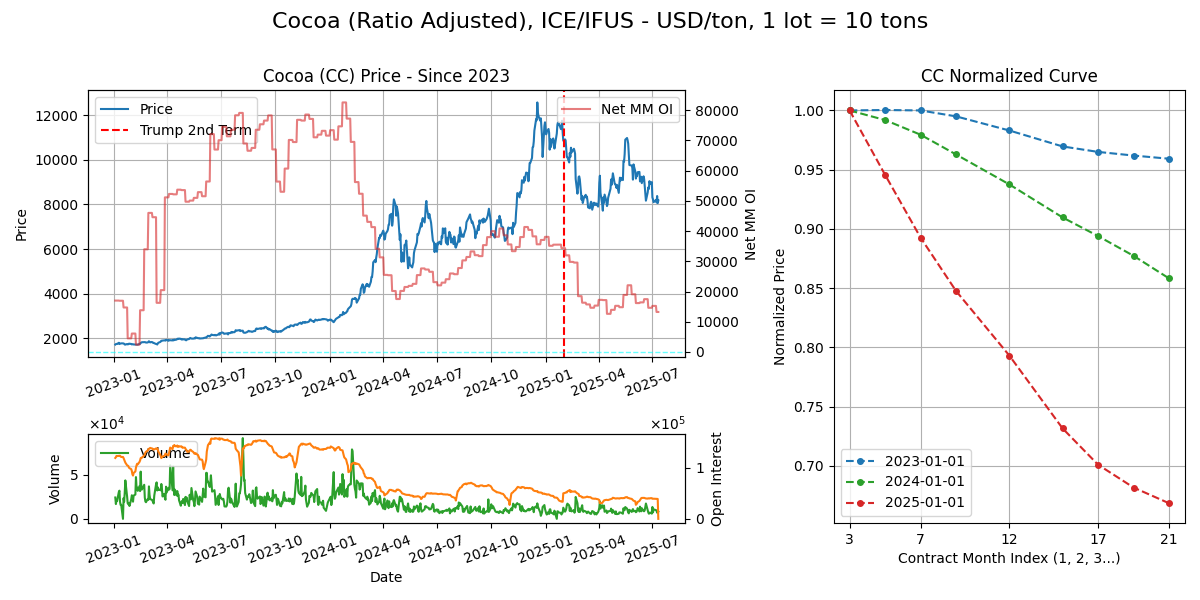
Calendar - 2Y out, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12. Last trading day one BD prior to LND, which is 10 BD prior to last BD of M. 8.45am-6.00pm GMT. Interestingly, cocoa is the only contract in past 2Y where MM got caught flat footed by a large amount, at the start of 2024.
Delivery - Delivery is of beans, the dried/fermented seed of cacao fruit from the tree. ICE divides cocoa into groups A (WAF) - +160/ton, B (SA/LATAM) +80, C (Asian) +0 to warehouses at various US ports.
Supply Chain
Climate - 20-30c but humid/wet climates, cannot tolerance frost/extreme heat. Hence tropicals.
Crop Cycle - A crop takes 5Y to bear pods, from 5-20 they continuously bear fruit. Two harvest peaks in rainy/monsoon periods: in West Africa, Oct-Mar (main crop) and Apr-Sep (mid-crop). Sensitive to weather extremes, too hot/drought or too rainy = black pod disease.
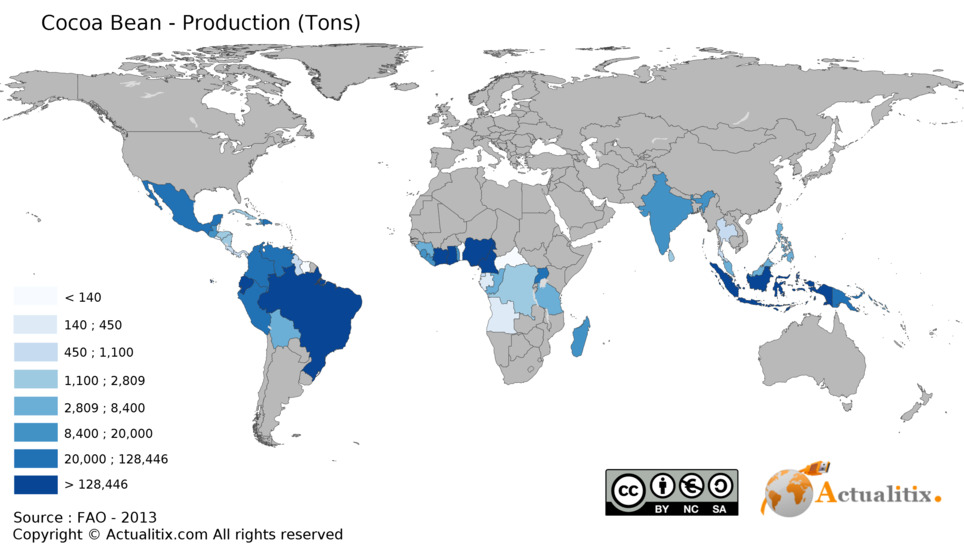
Major Export/Import: Exporters: West Africa (70%), Latam (25%), Asia (5%). Importers: EU (50%), US (20%), Asia (15%), with Malaysia being dominant in Asian bean imports. Roasting in import regions.
Arabica Coffee (C)
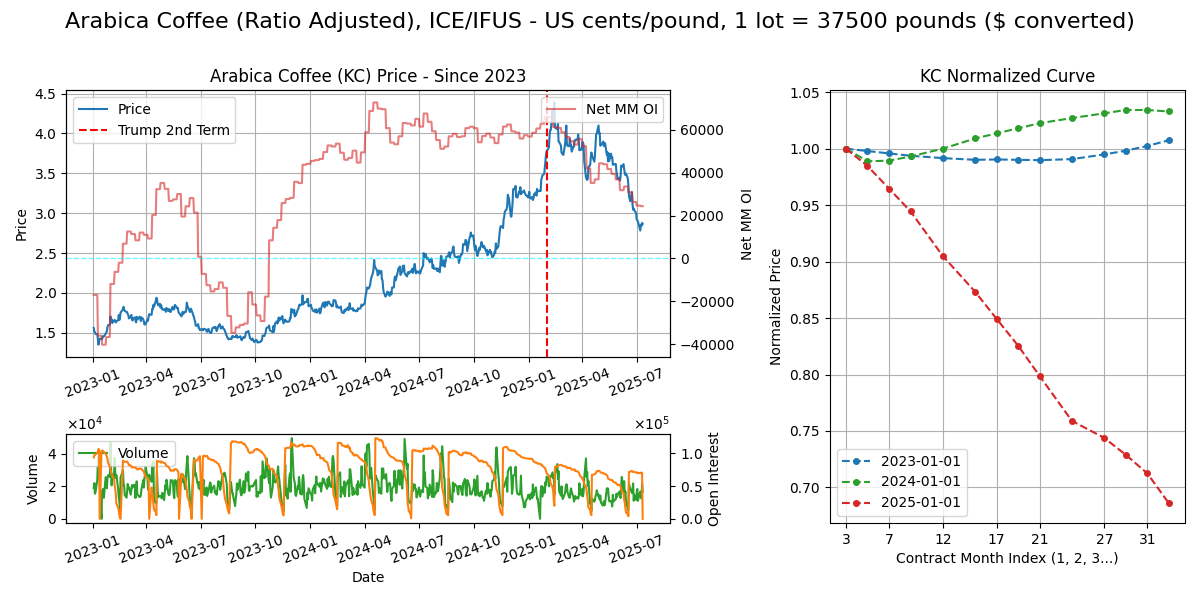
Calendar - 2Y out, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12. Last trading day one BD prior to LND, which is 7 BD prior to last BD of M. 8.45am-6.00pm GMT.
Delivery - At licensed US and EU (Bremen/Hamburg, Antwerp, Barcelona) warehouse ports, of green beans (processed seed of cherry)
Supply Chain
Climate - Arabica prefers slightly cooler, dryer climate than cocoa so 18-22c. Robusta prefers slightly warmer than arabica, 22-26c.
Crop Cycle - Takes 2Y from planting to bear fruit, and steady bearing comes in years 3-6. Cherries harvested when ripe (green to red). Harvest season May to Sep in Brazil.
Major Export/Import - Brazil A (40%), Vietnam R (20%), Colombia A (7%), Indonesia R (6%), Ethiopia A (5%), etc. Mostly LATAM, East Africa and SEA
Processing - Cherry > depulping > fermentation > drying > green bean > roasting and blending > roasted coffee bean. Roasting capacity mostly in US/EU.
Raw Sugar (SB)
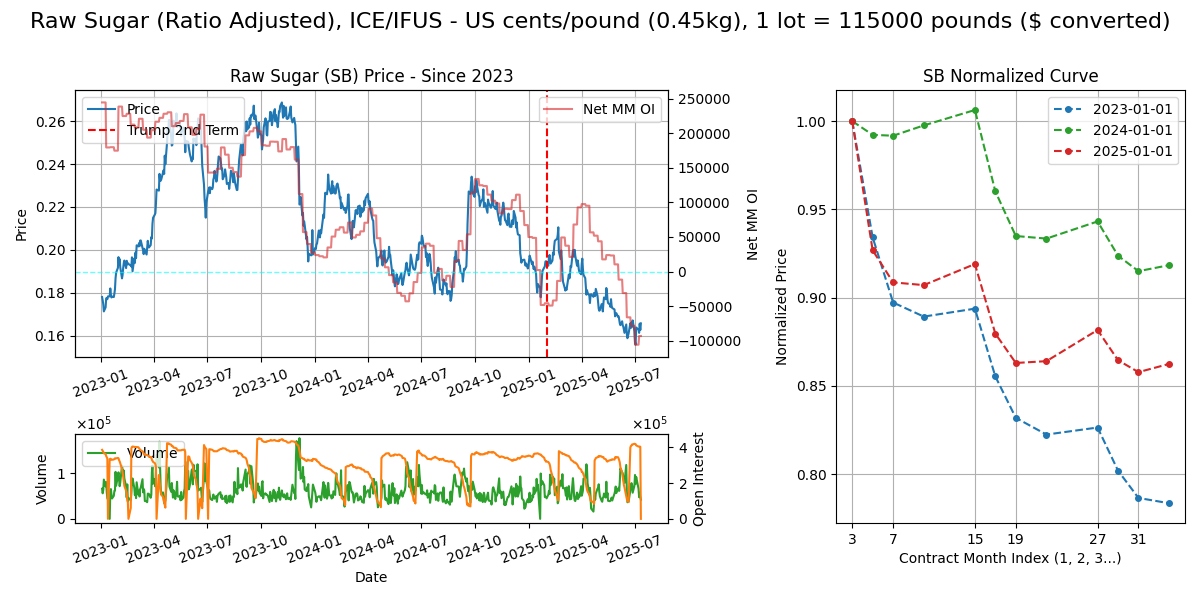
Calendar - 2Y out, 3, 5, 7, 10. 8.45am-6.00pm GMT.
Delivery - Raw centrifugal cane sugar FOB at a port in the origin of the growth.
Supply Chain
Processing - Canes and beets are harvested, crushed/evaporated into syrup and crystallized into rougher raw sugar crystals. Raw sugar is refined, turned to syrup and recrystallized into finer white sugar.
Climate - Beets prefer 15-21c in growing season (temperature) sugarcane prefers 20-35c in humid climates.
Crop Cycle - Beets take 2Y to flower but farmers cut the root after 1Y. Planting (Apr, May in spring), growing (June-Sep), harvest (Oct-Nov winter). Cane: harvested 12-15 months after planting per ratoon cycle, 3 ratoons with yields declining after each ratoon. Brazil sugarcane harvest season is in April extending to November, after rainy summer months. Reflected in March premium in curve structure, and harvesting season seen in NDVI drop.
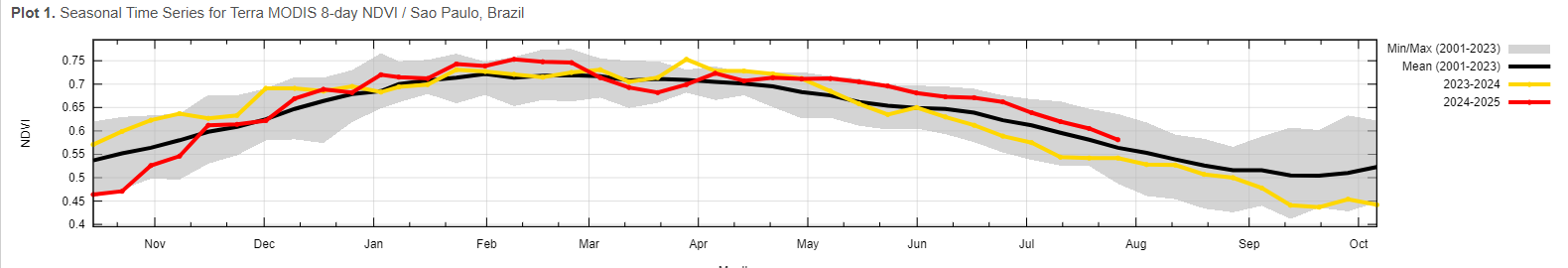
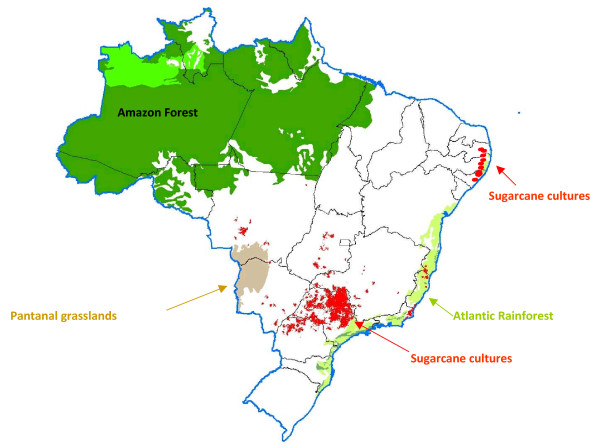
Export/Import - Brazil C (25%), Thailand C 10%, India C (7%), Germany C (7%), Guatemala C (5%), China C (5%). Brazil crop = 45mn tonnes, US crop = 10mn tonnes. Largest refining capacity: India (35 MMT), EU (25 MMT), China (15 MMT), US (10 MMT). Imports of raw and white sugar are balanced.
Produce
Lean Hogs (LE)
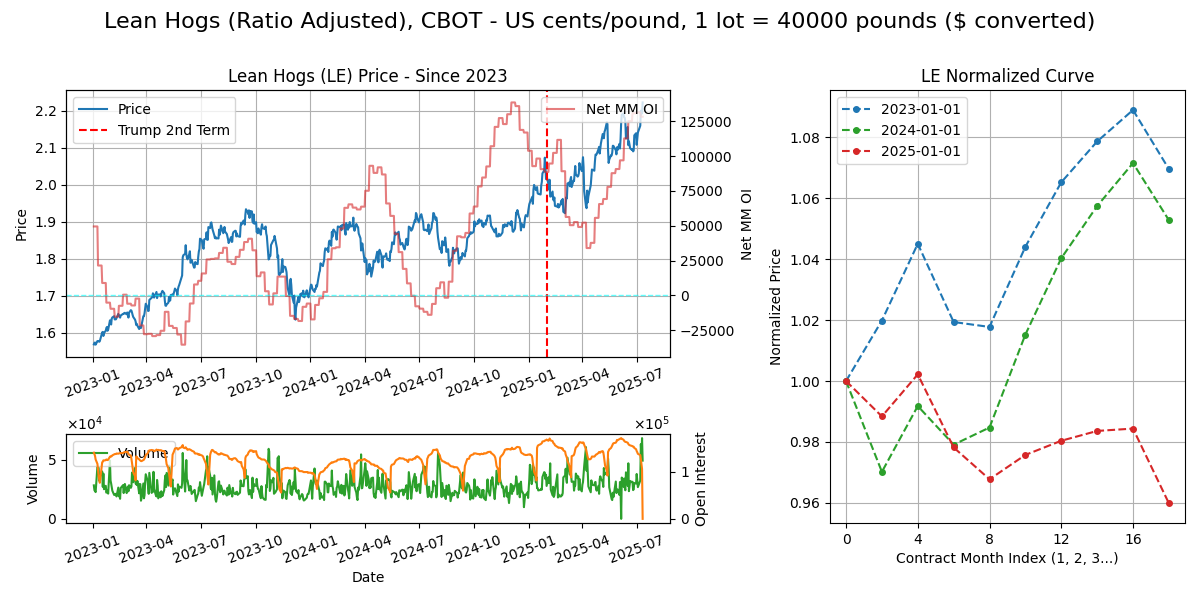
Calendar - 2Y out, 2, 4, 5, 6 7, 8, 12. Weekdays 8.30am-1.05pm CT or 2.30pm-7.05pm London, trading ends 10th BD of M.
Delivery - Financially settled.
Supply Chain
Processing - Hogs are slaughtered and processed into carcasses, cut, packaged and chilled then loaded into refrigerated trucks, rail or containers for distribution.
Export/Import (Pork) - Export: EU (30%), US (30%), Brazil (15%), Canada (5%), etc
Export/Import (Cattle/Beef) - EU (30%), US (30%), Brazil (25%), Australia (15%), India (7%), Argentina (5%), NZ (4%).